Oncolytic vaccinia virus harboring CLEC2A gene enhances viral replication and antitumor efficacy
- PMID: 39006946
- PMCID: PMC11239687
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omton.2024.200823
Oncolytic vaccinia virus harboring CLEC2A gene enhances viral replication and antitumor efficacy
Abstract
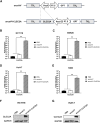
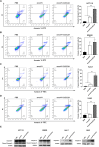
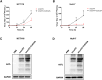
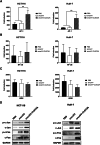
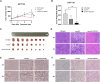
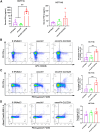
In the field of innovative cancer treatment strategies, oncolytic vaccinia virus (VV)es have gained traction as promising vectors. In the current study, we inserted the human C-type lectin domain family 2 member A (CLEC2A) gene into VV, creating a replicating therapeutic, oncoVV-CLEC2A. The findings reveal that oncoVV-CLEC2A effectively suppresses colorectal proliferation of mouse xenografts and a range of human cancer cell lines by augmenting viral reproduction capabilities, including the lung cancer H460 cell line, colorectal cancer cell lines (HCT116 and SW620), and hepatocellular carcinoma HuH-7 cell line. Moreover, it is evident that oncoVV-CLEC2A can induce antitumor immunity by boosting cytokine production but not antivirus response, and enhancing calreticulin expression. Further investigation indicates that oncoVV-CLEC2A can enhance antitumor capabilities by activating natural killer cells to produce interferon-γ and induce M1-like macrophage polarization. These findings shed light on the antitumor mechanisms of oncoVV-CLEC2A, provide a theoretical basis for oncolytic therapies, and lay the groundwork for novel strategies for modifying VVs.
Keywords: C-type lectin domain family 2 member A; MT: Regular Issue; NK cells; antitumor; oncolytic vaccinia virus; viral replication.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Jefferson A., Cadet V.E., Hielscher A. The mechanisms of genetically modified vaccinia viruses for the treatment of cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2015;95:407–416. - PubMed
-
- Smith G.L., Moss B. Infectious poxvirus vectors have capacity for at least 25 000 base pairs of foreign DNA. Gene. 1983;25:21–28. - PubMed
-
- Breitbach C.J., Burke J., Jonker D., Stephenson J., Haas A.R., Chow L.Q.M., Nieva J., Hwang T.H., Moon A., Patt R., et al. Intravenous delivery of a multi-mechanistic cancer-targeted oncolytic poxvirus in humans. Nature. 2011;477:99–102. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
