Ectopic Cushing syndrome in metastatic castration‑resistant prostate cancer: A case report and review of literature
- PMID: 39006947
- PMCID: PMC11240268
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2024.14550
Ectopic Cushing syndrome in metastatic castration‑resistant prostate cancer: A case report and review of literature
Abstract
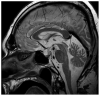
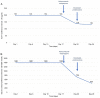
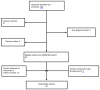
Cushing's syndrome (CS), as a result of ectopic adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) production, constitutes a common paraneoplastic manifestation of various malignancies, with the most common being small cell lung carcinoma. In the literature, fewer than fifty cases associating ectopic CS with prostate cancer have been documented. In the present study, the case of a 76-year old man suffering from castration-resistant prostate adenocarcinoma that had been treated with enzalutamide and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) analogue for the last four years is presented. The patient presented to the emergency department with lower extremity muscle weakness, bradypsychia and hypokalemia. Following a thorough diagnostic evaluation, hypercortisolemia was identified. No suppression after low- and high-dose dexamethasone challenge, increased cortisol 24 h excretion and normal pituitary magnetic resonance imaging led to the diagnosis of ectopic CS. Immediate targeted therapy was initiated with adrenal steroidogenesis inhibitors, including metyrapone and ketoconazole along with chemotherapy with docetaxel and prednisolone. There was a remarkable decrease in cortisol levels within days and hospitalization was no longer required. The patient managed to complete three cycles of chemotherapy; unfortunately, he succumbed within three months of the diagnosis of ectopic CS. In the present study, all existing cases of paraneoplastic CS related to prostate cancer are reviewed. The aim of the current study was to highlight the need of early diagnosis and treatment of this entity as it may present with atypical clinical findings and potentially evolve to a life-threatening condition.
Keywords: Cushing syndrome; ectopic adrenocorticotropic hormone; neuroendocrine dedifferentiation; paraneoplastic syndrome; prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2024, Spandidos Publications.
Conflict of interest statement
MAD has received honoraria from participation in advisory boards from Amgen, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Takeda. FZ has received honoraria for lectures and has served in an advisory role for Astra-Zeneca, Daiichi, Eli-Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
