Ameliorative effects of umbelliferone against acetaminophen-induced hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation in mice
- PMID: 39006976
- PMCID: PMC11244709
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-5362.394823
Ameliorative effects of umbelliferone against acetaminophen-induced hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation in mice
Abstract
Background and purpose: Acetaminophen (APAP) is a commonly used antipyretic and pain reliever that its overdose causes acute liver toxicity. Umbelliferone (UMB) has many pharmacological effects. In this study, the hepatoprotective effect of UMB on acute hepatotoxicity induced by APAP was investigated.
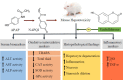
Experimental approach: Forty-nine male mice were separated into seven groups. The control received vehicle (i.p.), UMB group received UMB (120 mg/kg, i.p.), APAP group was treated with a single dose of APAP (350 mg/kg, i.p.), and pretreated groups received N-acetylcysteine (NAC, 200 mg/kg, i.p.) or different doses of UMB (30, 60, and 120 mg/kg, i.p.), respectively before APAP. Twenty-four hours after APAP injection, mice were sacrificed and blood and liver samples were collected. Then, serum and tissue samples were investigated for biochemical and histological studies.
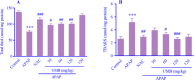
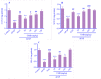
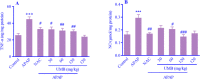
Findings/results: A single dose of APAP caused elevation in the serum liver enzymes, including alanine aminotransferase, aspartate transaminase, and alkaline phosphatase. The amounts of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and nitric oxide increased in the mice's liver tissue. Moreover, the amount of total thiol and the activity of antioxidant enzymes (catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione peroxidase) significantly diminished in the APAP group. Histological results confirmed the hepatotoxicity induced by APAP. However, UMB (more effective at 60 and 120 mg/kg) lessened APAP-induced hepatic injuries, which is comparable with NAC effects.
Conclusion and implications: The findings of this study provided evidence that UMB ameliorates liver injury induced by APAP through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Keywords: Acetaminophen; Hepatotoxicity; Inflammation; Oxidative stress; Umbelliferone..
Copyright: © 2024 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protective Effects of Tormentic Acid, a Major Component of Suspension Cultures of Eriobotrya japonica Cells, on Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice.Molecules. 2017 May 18;22(5):830. doi: 10.3390/molecules22050830. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28524081 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Fresh/Dry Dandelion Extracts on APAP-Overdose-Induced Acute Liver Injury.Chin J Integr Med. 2022 Aug;28(8):683-692. doi: 10.1007/s11655-021-3295-8. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Chin J Integr Med. 2022. PMID: 34816363
-
Therapeutic effect of liposomal-N-acetylcysteine against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity.J Drug Target. 2013 May;21(5):466-73. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2013.765443. Epub 2013 Apr 19. J Drug Target. 2013. PMID: 23600745
-
Hepatoprotective Activity of Yellow Chinese Chive against Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury via Nrf2 Signaling Pathway.J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2020;66(4):357-363. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.66.357. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2020. PMID: 32863309
-
Can granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) ameliorate acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity?Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021 Oct;40(10):1755-1766. doi: 10.1177/09603271211008522. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33882750
Cited by
-
Bilirubin, once a toxin but now an antioxidant alleviating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in an autophagy-dependent manner in high-fat diet-induced rats: a molecular and histopathological analysis.Res Pharm Sci. 2024 Aug 19;19(4):475-488. doi: 10.4103/RPS.RPS_53_24. eCollection 2024 Aug. Res Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 39399727 Free PMC article.
-
Quinic acid alleviates liver toxicity induced by acetaminophen in mice via anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;398(8):10367-10378. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03869-7. Epub 2025 Feb 22. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39985580
-
Aloperine Ameliorates Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury through HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB and NLRP3/Inflammasome Pathway.Mediators Inflamm. 2024 Oct 1;2024:3938136. doi: 10.1155/2024/3938136. eCollection 2024. Mediators Inflamm. 2024. PMID: 39381066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ren YS, Zheng Y, Duan H, Lei L, Deng X, Liu XQ, et al. Dandelion polyphenols protect against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice via activation of the Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway and inhibition of the JNK signaling pathway. Chin J Nat Med. 2020;18(2):103–113. DOI: 10.1016/S1875-5364(20)30011-X. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
