The therapeutic value of thiazole and thiazolidine derivatives in Alzheimer's disease: a systematic literature review
- PMID: 39006977
- PMCID: PMC11244712
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-5362.394816
The therapeutic value of thiazole and thiazolidine derivatives in Alzheimer's disease: a systematic literature review
Abstract
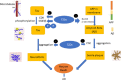
Background and purpose: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a common neurodegenerative disease and the fifth leading cause of death among the elderly. The development of drugs for AD treatment is based on inhibiting cholinesterase (ChE) activity and inhibiting amyloid-beta peptide and tau protein aggregations. Many in vitro findings have demonstrated that thiazole-and thiazolidine-based compounds have a good inhibitory effect on ChE and other elements involved in the AD pathogenicity cascade.
Experimental approach: In the present review, we collected available documents to verify whether these synthetic compounds can be a step forward in developing new medications for AD. A systematic literature search was performed in major electronic databases in April 2021. Twenty-eight relevant in vitro and in vivo studies were found and used for data extraction.
Findings/results: Findings demonstrated that thiazole-and thiazolidine-based compounds could ameliorate AD's pathologic condition by affecting various targets, including inhibition of ChE activity, amyloid-beta, and tau aggregation in addition to cyclin-dependent kinase 5/p25, beta-secretase-1, cyclooxygenase, and glycogen synthase kinase-3β.
Conclusion and implications: Due to multitarget effects at micromolar concentration, this review demonstrated that these synthetic compounds could be considered promising candidates for developing anti-Alzheimer drugs.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Amyloid beta; Cholinesterase; Glycogen synthase kinase; Thiazole.; Thiazolidine.
Copyright: © 2024 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of bergenin in Alzheimer's disease: Investigation through molecular docking, in vitro and in vivo studies.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Jan 1;356:18-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.08.010. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30118774
-
Flavonoids as therapeutic compounds targeting key proteins involved in Alzheimer's disease.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014 Feb 19;5(2):83-92. doi: 10.1021/cn400213r. Epub 2014 Jan 3. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24328060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neurobiology and therapeutic potential of multi-targeting β-secretase, glycogen synthase kinase 3β and acetylcholinesterase in Alzheimer's disease.Ageing Res Rev. 2023 Sep;90:102033. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2023.102033. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Ageing Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 37595640 Review.
-
Fused thiophene as a privileged scaffold: A review on anti-Alzheimer's disease potentials via targeting cholinesterases, monoamine oxidases, glycogen synthase kinase-3, and Aβ aggregation.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;265(Pt 2):131018. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131018. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38518928 Review.
-
Therapeutic implications of glycogen synthase kinase-3β in Alzheimer's disease: a novel therapeutic target.Int J Neurosci. 2024 Jun;134(6):603-619. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2022.2130297. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Int J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 36178363 Review.
Cited by
-
The novel orthosteric agonist M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor reveals anti-Alzheimer's disease activity.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 21;14(1):28824. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80102-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39572774 Free PMC article.
-
d‑Glucose-Conjugated Benzo[d]thiazole-thiazolidin-4-one Hybrids: Design and Synthesis as Multitarget Anti-Alzheimer Compounds.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2025 May 5;16(6):1024-1030. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5c00064. eCollection 2025 Jun 12. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2025. PMID: 40529084
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
