Clinicopathological correlation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 and their death receptor in patients with gastric cancer
- PMID: 39006978
- PMCID: PMC11244704
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-5362.394819
Clinicopathological correlation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 and their death receptor in patients with gastric cancer
Abstract
Background and purpose: The insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3) and its novel death receptor (IGFBP-3R) have been exhibited to have tumor suppressor effects. Despite their prognostic value in some cancers, they have not been elucidated in gastric cancer.
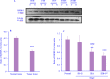
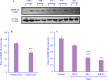
Experimental approach: We collected 68 samples from patients with gastric cancer. IGFBP-3 and IGFBP-3R expression levels were evaluated with quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and western blotting in patients. The relationship between prognostic factors and IGFBP-3/IGFBP-3R expression was also evaluated.
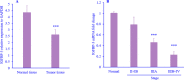
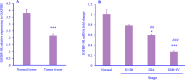
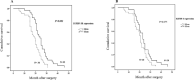
Findings/results: Our results showed that IGFBP-3 and IGFBP-3R expression was reduced significantly in tumor tissues. We found that there was an association between the reduction of IGFBP-3 with lymph node metastasis and tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging. Besides, IGFBP-3R expression was associated with tumor size, lymph node metastasis, differentiation, and TNM classification. Interestingly, we presented that the downregulation of IGFBP-3R was stage-dependent. In survival analysis, our findings showed that low levels of IGFBP-3R mRNA expression exhibited a close correlation with survival rate.
Conclusion and implications: The findings of this study showed that the expression levels of IGFBP-3 and IGFBP-3R are valuable prognostic factors. Despite the potential of IGFBP-3, IGFBP-3R plays a significant role as a prognostic factor in gastric cancer. However, these findings need to be developed and confirmed by further studies.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; IGFBP-3; IGFBP-3R; Prognostic factor; TNM classification..
Copyright: © 2024 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures
References
-
- Chua YJ, Cunningham D. The UK NCRI MAGIC trial of perioperative chemotherapy in resectable gastric cancer: implications for clinical practice. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14(10):2687–2690. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-007-9423-7. - PubMed
-
- Abbas M, Habib M, Naveed M, Karthik K, Dhama K, Shi M, et al. The relevance of gastric cancer biomarkers in prognosis and pre-and post-chemotherapy in clinical practice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;95:1082–1090. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.09.032. - PubMed
-
- Ranke MB. Insulin-like growth factor binding-protein-3 (IGFBP-3) Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol. 2015;29(5):701–711. DOI: 10.1016/j.beem.2015.06.003. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
