A Proof of Concept Study on the Comfort and Usability of a Supportive Pillow for Pregnant Patients with COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- PMID: 39006984
- PMCID: PMC11239996
- DOI: 10.47895/amp.v58i11.8593
A Proof of Concept Study on the Comfort and Usability of a Supportive Pillow for Pregnant Patients with COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Abstract
Background: The prone position has been seen to benefit patients experiencing acute respiratory distress syndrome. However, performing this position in pregnant patients has been difficult and raises safety concerns.
Objective: The current study aimed to test the use of a supportive pillow (Prone Pillow for Pregnant Patients or 4P) to address concerns regarding pregnant patients in prone position.
Methods: The study prospectively evaluated the use of the prone pillow for patient comfort and usability among healthcare workers with qualitative and quantitative measures.
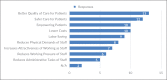
Results: A total of three patients were recruited alongside 16 healthcare workers assisting pregnant patients to the prone position. Overall, awake pregnant patients found the pillow to be comfortable while healthcare workers perceived the pillow to be useful in improving quality of care among awake and intubated pregnant patients.
Conclusion: The 4P is a potentially useful and beneficial product in placing pregnant patients in the prone position during episodes of acute respiratory distress. However, due to the limited sample size, more clinical trials are needed to evaluate the impact of this innovation in improving patient and healthcare worker safety.
Keywords: ARDS; COVID-19; prone pillow; prone positioning.
© 2024 Acta Medica Philippina.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- CoronaTracker [Internet]. October 31, 2022. [cited 2022 Oct 21]. Available from: https://www.coronatracker.com/analytics
-
- Department of Health . COVID-19 Tracker [Internet]. October 31, 2020. [cited 2022 Oct 21]. Available from: https://www.doh.gov.ph/covid19tracker.
-
- Fan E, Beitler JR, Brochard L, Calfee CS, Ferguson ND, Slutsky AS, et al. COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: is a different approach to management warranted? Lancet Respir Med. 2020. Aug;8(8):816-21. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30304-0. PMID: 32645311; PMCID: . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meftahi N, Bervis S, Taghizadeh S, Ghafarinejad F. The effect of lying in prone position on blood pressure and heart rate with and without massage. J Rehab Sci Res. 2014;1(2):40-3.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
