Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway as an important mediator in muscle and bone crosstalk: A systematic review
- PMID: 39007034
- PMCID: PMC11245956
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.06.003
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway as an important mediator in muscle and bone crosstalk: A systematic review
Abstract
Background: The interaction between muscle and bone is shown to be clinically important but the underlying mechanisms are largely unknown. The canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is reported to be involved in muscle-bone crosstalk, but its detailed function remains unclear. This systematic review aims to investigate and elucidate the role of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in muscle-bone crosstalk.
Methods: We conducted a literature search on the Web of Science, PubMed, EBSCO and Embase with keywords "Wnt*", "bone*" and "muscle*". A systematic review was completed according to the guideline of preferred reporting items of systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA). Data synthesis included species (human, animal or cell type used), treatments involved, outcome measures and key findings with respect to Wnts.
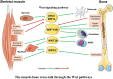
Results: Seventeen papers were published from 2007 to 2021 and were extracted from a total of 1529 search results in the databases of Web of Science (468 papers), PubMed (457 papers), EBSCO (371) and Embase (233). 12 Wnt family members were investigated in the papers, including Wnt1, Wnt2, Wnt2b, Wnt3a, Wnt4, Wnt5a, Wnt8a, Wnt8b, Wnt9a, Wnt10a, Wnt10b and Wnt16. Many studies showed that muscles were able to increase or decrease osteogenesis of bone, while bone increased myogenesis of muscle through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. Wnt3a, Wnt4 and Wnt10b were shown to play important roles in the crosstalk between muscle and bone.
Conclusions: Wnt3a, Wnt4 and Wnt10b are found to play important mediatory roles in muscle-bone crosstalk. The role of Wnt4 was mostly found to regulate muscle from the bone side. Whilst the role of Wnt10b during muscle ageing was proposed, current evidence is insufficient to clarify the specific role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the interplay between sarcopenia and osteoporosis. More future studies are required to investigate the exact regulatory roles of Wnts in muscle-bone crosstalk in musculoskeletal disease models such as sarcopenia and osteoporosis.
Translational potential of this article: The systematic review provides an extensive overview to reveal the roles of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in muscle-bone crosstalk. These results provide novel research directions to further understand the underlying mechanism of sarcopenia, osteoporosis, and their crosstalk, finally helping the future development of new therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: Bone; Crosstalk; Muscle; Osteoporosis; Sarcopenia; Wnt/β-catenin.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest relevant to this review.
Figures


References
-
- Sjoblom S., Suuronen J., Rikkonen T., Honkanen R., Kroger H., Sirola J. Relationship between postmenopausal osteoporosis and the components of clinical sarcopenia. Maturitas. 2013;75(2):175–180. - PubMed
-
- Kanis J.A. Diagnosis of osteoporosis and assessment of fracture risk. Lancet. 2002;359(9321):1929–1936. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

