Ethnic differences in the effects of apolipoprotein E ɛ4 and vascular risk factors on accelerated brain aging
- PMID: 39007039
- PMCID: PMC11242459
- DOI: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae213
Ethnic differences in the effects of apolipoprotein E ɛ4 and vascular risk factors on accelerated brain aging
Abstract
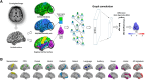
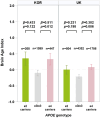
The frequency of the apolipoprotein E ɛ4 allele and vascular risk factors differs among ethnic groups. We aimed to assess the combined effects of apolipoprotein E ɛ4 and vascular risk factors on brain age in Korean and UK cognitively unimpaired populations. We also aimed to determine the differences in the combined effects between the two populations. We enrolled 2314 cognitively unimpaired individuals aged ≥45 years from Korea and 6942 cognitively unimpaired individuals from the UK, who were matched using propensity scores. Brain age was defined using the brain age index. The apolipoprotein E genotype (ɛ4 carriers, ɛ2 carriers and ɛ3/ɛ3 homozygotes) and vascular risk factors (age, hypertension and diabetes) were considered predictors. Apolipoprotein E ɛ4 carriers in the Korean (β = 0.511, P = 0.012) and UK (β = 0.302, P = 0.006) groups had higher brain age index values. The adverse effects of the apolipoprotein E genotype on brain age index values increased with age in the Korean group alone (ɛ2 carriers × age, β = 0.085, P = 0.009; ɛ4 carriers × age, β = 0.100, P < 0.001). The apolipoprotein E genotype, age and ethnicity showed a three-way interaction with the brain age index (ɛ2 carriers × age × ethnicity, β = 0.091, P = 0.022; ɛ4 carriers × age × ethnicity, β = 0.093, P = 0.003). The effects of apolipoprotein E on the brain age index values were more pronounced in individuals with hypertension in the Korean group alone (ɛ4 carriers × hypertension, β = 0.777, P = 0.038). The apolipoprotein E genotype, age and ethnicity showed a three-way interaction with the brain age index (ɛ4 carriers × hypertension × ethnicity, β=1.091, P = 0.014). We highlight the ethnic differences in the combined effects of the apolipoprotein E ɛ4 genotype and vascular risk factors on accelerated brain age. These findings emphasize the need for ethnicity-specific strategies to mitigate apolipoprotein E ɛ4-related brain aging in cognitively unimpaired individuals.
Keywords: APOE ɛ4; brain age; ethnicity; vascular risk factors.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Lind J, Larsson A, Persson J, et al. Reduced hippocampal volume in non-demented carriers of the apolipoprotein E epsilon4: Relation to chronological age and recognition memory. Neurosci Lett. 2006;396(1):23–27. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
