Pericyte derivation and transplantation for blood-CNS barrier reconstitution in CNS disorders
- PMID: 39007089
- PMCID: PMC11240299
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2023.12.007
Pericyte derivation and transplantation for blood-CNS barrier reconstitution in CNS disorders
Abstract
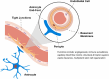
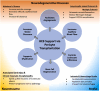
Disruption of the blood-central nervous system barrier (BCB) is increasingly recognized as a pathological factor in diseases and trauma of the central nervous system. Despite the neuropathological impact, current treatment modalities do not target the BCB; strategies to reconstitute the impaired BCB have been restricted to nutritional and dietary remedies. As an integral cell type in the neurovascular unit, pericytes are crucial to the development, maintenance, and repair of the BCB. As such, pericytes are well poised as cellular agents for reconstitution of the impaired BCB. Here, we summarize recent revelations regarding the role of BCB disruption in diseases and trauma of the central nervous system and highlight how pericytes are harnessed to provide targeted therapeutic effect in each case. This review will also address how recent advances in pericyte derivation strategies can serve to overcome practical hurdles in the clinical use of pericytes.
Keywords: Adult stem cells; Blood-CNS barrier; Cell therapy; Pericytes.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Amos P.J., Mulvey C.L., Seaman S.A., Walpole J., Degen K.E., Shang H., Katz A.J., Peirce S.M. Hypoxic culture and in vivo inflammatory environments affect the assumption of pericyte characteristics by human adipose and bone marrow progenitor cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011;301 doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00460.2010. C1378-88. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
