Design and expression of a chimeric recombinant antigen (SsIR-Ss1a) for the serodiagnosis of human strongyloidiasis: Evaluation of performance, sensitivity, and specificity
- PMID: 39008519
- PMCID: PMC11271862
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012320
Design and expression of a chimeric recombinant antigen (SsIR-Ss1a) for the serodiagnosis of human strongyloidiasis: Evaluation of performance, sensitivity, and specificity
Erratum in
-
Correction: Design and expression of a chimeric recombinant antigen (SsIR-Ss1a) for the serodiagnosis of human strongyloidiasis: Evaluation of performance, sensitivity, and specificity.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025 Jan 29;19(1):e0012838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012838. eCollection 2025 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025. PMID: 39879155 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The sensitivity of parasitological and molecular methods is unsatisfactory for the diagnosis of strongyloidiasis, and serological techniques are remaining as the most effective diagnostic approach. The present study aimed to design and produce a chimeric recombinant antigen from Strongyloides stercoralis immunoreactive antigen (SsIR) and Ss1a antigens, using immune-informatics approaches, and evaluated its diagnostic performance in an ELISA system for the diagnosis of human strongyloidiasis.
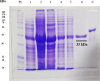
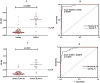
Methodology/principal findings: The coding sequences for SsIR and Ss1a were selected from GenBank and were gene-optimized. Using bioinformatics analysis, the regions with the highest antigenicity that did not overlap with other parasite antigens were selected. The chimeric recombinant antigen SsIR- Ss1a, was constructed. The solubility and physicochemical properties of the designed construct were analyzed and its tertiary structures were built and evaluated. The construct was expressed into the pET-23a (+) expression vector and the optimized DNA sequences of SsIR-Ss1a (873 bp) were cloned into competent E. coli DH5α cells. Diagnostic performances of the produced recombinant antigen, along with a commercial kit were evaluated in an indirect ELISA system, using a panel of sera from strongyloidiasis patients and controls. The physicochemical and bioinformatics evaluations revealed that the designed chimeric construct is soluble, has a molecular with of 35 KDa, and is antigenic. Western blotting confirmed the immunoreactivity of the produced chimeric recombinant antigen with the sera of strongyloidiasis patients. The sensitivity and specificity of the indirect ELISA system, using the produced SsIR-Ss1a chimeric antigen, were found to be 93.94% (95% CI, 0.803 to 0.989) and 97.22% (95% CI, 0.921 to 0.992) respectively.
Conclusions/significance: The preliminary findings of this study suggest that the produced SsIR-Ss1a chimeric antigen shows promise in the diagnosis of human strongyloidiasis. However, these results are based on a limited panel of samples, and further research with a larger sample size is necessary to confirm its accuracy. The construct has potential as an antigen in the ELISA system for the serological diagnosis of this neglected parasitic infection, but additional validation is required.
Copyright: © 2024 Omidian et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Diagnostic accuracy of a novel enzyme-linked immunoassay for the detection of IgG and IgG4 against Strongyloides stercoralis based on the recombinant antigens NIE/SsIR.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Aug 18;14(1):412. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04916-x. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 34407876 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral Flow Dipstick Test for Serodiagnosis of Strongyloidiasis.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019 Aug;101(2):432-435. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.19-0053. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019. PMID: 31218996 Free PMC article.
-
Improved diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis using recombinant antigen-based serologies in a community-wide study in northern Argentina.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010 Oct;17(10):1624-30. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00259-10. Epub 2010 Aug 25. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20739501 Free PMC article.
-
Serodiagnosis and early detection of Strongyloides stercoralis infection.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2019 Jun;52(3):371-378. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2018.10.001. Epub 2018 Oct 11. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2019. PMID: 30482708 Review.
-
Screening of Strongyloides infection using an ELISA test in transplant candidates.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2019;74:e698. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2019/e698. Epub 2019 Jun 6. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2019. PMID: 31188909 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Designing of a Multi-Epitope Antigen for Toxocariasis Diagnosis: An in Silico Approach.Acta Parasitol. 2025 Apr 8;70(2):85. doi: 10.1007/s11686-025-01027-w. Acta Parasitol. 2025. PMID: 40198410
-
Correction: Design and expression of a chimeric recombinant antigen (SsIR-Ss1a) for the serodiagnosis of human strongyloidiasis: Evaluation of performance, sensitivity, and specificity.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025 Jan 29;19(1):e0012838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012838. eCollection 2025 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025. PMID: 39879155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kikuchi T, Hino A, Tanaka T, Aung MPPTHH, Afrin T, Nagayasu E, et al.. Genome-wide analyses of individual Strongyloides stercoralis (Nematoda: Rhabditoidea) provide insights into population structure and reproductive life cycles. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 2016;10(12):e0005253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005253 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

