Emerging role of oncogenic ß-catenin in exosome biogenesis as a driver of immune escape in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 39008536
- PMCID: PMC11249736
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.95191
Emerging role of oncogenic ß-catenin in exosome biogenesis as a driver of immune escape in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
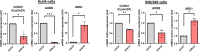
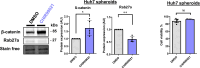
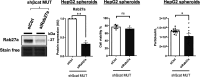
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have produced encouraging results in cancer patients. However, the majority of ß-catenin-mutated tumors have been described as lacking immune infiltrates and resistant to immunotherapy. The mechanisms by which oncogenic ß-catenin affects immune surveillance remain unclear. Herein, we highlighted the involvement of ß-catenin in the regulation of the exosomal pathway and, by extension, in immune/cancer cell communication in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We showed that mutated ß-catenin represses expression of SDC4 and RAB27A, two main actors in exosome biogenesis, in both liver cancer cell lines and HCC patient samples. Using nanoparticle tracking analysis and live-cell imaging, we further demonstrated that activated ß-catenin represses exosome release. Then, we demonstrated in 3D spheroid models that activation of β-catenin promotes a decrease in immune cell infiltration through a defect in exosome secretion. Taken together, our results provide the first evidence that oncogenic ß-catenin plays a key role in exosome biogenesis. Our study gives new insight into the impact of ß-catenin mutations on tumor microenvironment remodeling, which could lead to the development of new strategies to enhance immunotherapeutic response.
Keywords: cancer; cancer biology; cell biology; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; human; liver; ß-catenin.
© 2024, Dantzer et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CD, JV, AB, IM, AR, JD, MP, PB, DP, ND, MV, BB, CB, VM No competing interests declared
Figures



















Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2023.10.24.563805
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.95191.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.95191.2
References
-
- Akasu M, Shimada S, Kabashima A, Akiyama Y, Shimokawa M, Akahoshi K, Kudo A, Yamaoka S, Tanabe M, Tanaka S. Intrinsic activation of β-catenin signaling by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated exon skipping contributes to immune evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Scientific Reports. 2021;11:16732. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96167-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bakr M, Jullié D, Krapivkina J, Paget-Blanc V, Bouit L, Petersen JD, Retailleau N, Breillat C, Herzog E, Choquet D, Perrais D. The vSNAREs VAMP2 and VAMP4 control recycling and intracellular sorting of post-synaptic receptors in neuronal dendrites. Cell Reports. 2021;36:109678. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109678. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berchem G, Noman MZ, Bosseler M, Paggetti J, Baconnais S, Le Cam E, Nanbakhsh A, Moussay E, Mami-Chouaib F, Janji B, Chouaib S. Hypoxic tumor-derived microvesicles negatively regulate NK cell function by a mechanism involving TGF-β and miR23a transfer. Oncoimmunology. 2016;5:e1062968. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1062968. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

