Results of comprehensive genetic testing in patients presenting to a multidisciplinary inherited heart disease clinic in India
- PMID: 39009076
- PMCID: PMC11451389
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ihj.2024.07.002
Results of comprehensive genetic testing in patients presenting to a multidisciplinary inherited heart disease clinic in India
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to analyze the results of comprehensive genetic testing in patients presenting to a dedicated multidisciplinary inherited heart disease clinic in India.
Methods: All patients presenting to our clinic from August 2017 to October 2023 with a suspected inherited heart disease and consenting for genetic testing were included. The probands were grouped into familial cardiomyopathies namely hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM) and peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM), channelopathies namely congenital long QT syndrome (LQTS) and Brugada syndrome (BrS), and heritable connective tissue disorder namely Marfan Syndrome (MFS). Next generation sequencing (NGS) was used, and pre-test and post-test counseling were provided to probands and cascade screening offered to relatives.
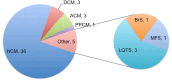
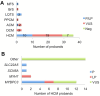
Results: Mean age of the subjects (n = 77; 48 probands, 29 relatives) was 43 ± 18 years, 68 % male and 44 % symptomatic, with 36 HCM, 3 DCM, 3 ACM, 1 PPCM, 3 LQTS, 1 BrS and 1 MFS probands. The diagnostic yield of NGS-based genetic testing was 31 %; variants of uncertain significance (VUS) were identified in 54 %; and 15 % were genotype-negative. Twenty-nine relatives from 18 families with HCM (n = 12), DCM (n = 3), ACM (n = 2) and MFS (n = 1) underwent genetic testing. The genotype positive probands/relatives and VUS carriers with strong disease phenotype and/or high risk variant were advised periodic follow-up; the remaining probands/relatives were discharged from further clinical surveillance.
Conclusions: Genetic testing guides treatment and follow-up of patients with inherited heart diseases and should be carried out in dedicated multidisciplinary clinics with expertise for counseling and cascade screening of family members.
Keywords: Cardiomyopathies; Channelopathies; Genetic testing; Multidisciplinary clinic; Sudden cardiac death prevention.
Copyright © 2024 Cardiological Society of India. Published by Elsevier, a division of RELX India, Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Maron B.J., Kalra A. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in the developing world: focus on India. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2492–2495. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical