High-flow nasal oxygen therapy compared with conventional oxygen therapy in hospitalised patients with respiratory illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39009460
- PMCID: PMC11268052
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjresp-2024-002342
High-flow nasal oxygen therapy compared with conventional oxygen therapy in hospitalised patients with respiratory illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: High-flow nasal oxygen therapy (HFNO) is used in diverse hospital settings to treat patients with acute respiratory failure (ARF). This systematic review aims to summarise the evidence regarding any benefits HFNO therapy has compared with conventional oxygen therapy (COT) for patients with ARF.
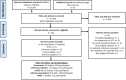
Methods: Three databases (Embase, Medline and CENTRAL) were searched on 22 March 2023 for studies evaluating HFNO compared with COT for the treatment of ARF, with the primary outcome being hospital mortality and secondary outcomes including (but not limited to) escalation to invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) or non-invasive ventilation (NIV). Risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool (randomised controlled trials (RCTs)), ROBINS-I (non-randomised trials) or Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (observational studies). RCTs and observational studies were pooled together for primary analyses, and secondary analyses used RCT data only. Treatment effects were pooled using the random effects model.
Results: 63 studies (26 RCTs, 13 cross-over and 24 observational studies) were included, with 10 230 participants. There was no significant difference in the primary outcome of hospital mortality (risk ratio, RR 1.08, 95% CI 0.93 to 1.26; p=0.29; 17 studies, n=5887) between HFNO and COT for all causes ARF. However, compared with COT, HFNO significantly reduced the overall need for escalation to IMV (RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.76 to 0.95 p=0.003; 39 studies, n=8932); and overall need for escalation to NIV (RR 0.70, 95% CI 0.50 to 0.98; p=0.04; 16 studies, n=3076). In subgroup analyses, when considering patients by illness types, those with acute-on-chronic respiratory failure who received HFNO compared with COT had a significant reduction in-hospital mortality (RR 0.58, 95% CI 0.37 to 0.91; p=0.02).
Discussion: HFNO was superior to COT in reducing the need for escalation to both IMV and NIV but had no impact on the primary outcome of hospital mortality. These findings support recommendations that HFNO may be considered as first-line therapy for ARF.
Prospero registration number: CRD42021264837.
Keywords: COPD Exacerbations; COVID-19; Critical Care; Non invasive ventilation; Pneumonia.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: YHK reports in-kind trial support from Air Liquide Healthcare, outside this project. NS reports receiving grant funding from Fisher & Paykel Healthcare for an investigator-initiated research study outside this project. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Sharma S, Danckers M, Sanghavi D, et al. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): 2022. High flow nasal Cannula.
-
- Pacheco E, Wawrzeniak IC, Victorino JA, et al. Physiological effects of high flow nasal therapy in patients with acute respiratory failure measured by esophageal catheter and electrical impedance tomography: a pilot study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;119 doi: 10.1164/ajrccm-conference.2019.199.1_MeetingAbstracts.A2735. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
