Oxidative and carbonyl stress induced AMD and Codonopsis lanceolata ameliorates AMD via controlling oxidative and carbonyl stress
- PMID: 39009704
- PMCID: PMC11251066
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-67044-3
Oxidative and carbonyl stress induced AMD and Codonopsis lanceolata ameliorates AMD via controlling oxidative and carbonyl stress
Abstract
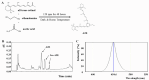
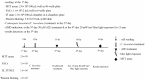
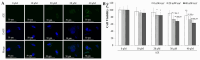
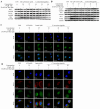
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is one of the leading causes of blindness. AMD is currently incurable; the best solution is to prevent its occurrence. To develop drugs for AMD, it is crucial to have a model system that mimics the symptoms and mechanisms in patients. It is most important to develop safer and more effective anti-AMD drug. In this study, the dose of A2E and the intensity of blue light were evaluated to establish an appropriate atrophic in vitro model of AMD and anti-AMD effect and therapeutic mechanism of Codonopsis lanceolata. The experimental groups included a control group an AMD group treated with A2E and blue light, a lutein group treated with 25 μM lutein after AMD induction, and three groups treated with different doses of C. lanceolata (10, 20, and 50 μg/mL) after AMD induction. Intrinsic apoptotic pathway (Bcl-2 family), anti-oxidative system (Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant response element), and anti-carbonyl effect (4-hydroxynonenal [4-HNE]) were evaluated using immunofluorescence, MTT, TUNEL, FACS, and western blotting analyses. A2E accumulation in the cytoplasm of ARPE-19 cells depending on the dose of A2E. Cell viability of ARPE-19 cells according to the dose of A2E and/or blue light intensity. The population of apoptotic or necrotic cells increased based on the A2E dose and blue light intensity. Codonopsis lanceolata dose-dependently prevented cell death which was induced by A2E and blue light. The antiapoptotic effect of that was caused by activating Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, suppressing 4-HNE, and modulating Bcl-2 family proteins like increase of antiapoptotic proteins such as Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL and decrease of proapoptotic protein such as Bim. Based on these findings, 30 μM A2E and 20 mW/cm2 blue light on adult retinal pigment epithelium-19 cells was an appropriate condition for AMD model and C. lanceolata shows promise as an anti-AMD agent.
Keywords: Codonopsis lanceolata; 4-HNE; Age-related macular degeneration (AMD); Apoptosis; Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway; Oxidative/carbonyl stress.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Jonas JB, et al. Updates on the epidemiology of age-related macular degeneration. Asia-Pac J. Ophthalmol. 2017;6:493–497. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization, Ageing and health. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health. Accessed 26th Jan 2023 (2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

