Immunosuppression in adult liver transplant recipients: a 2024 update from the Italian Liver Transplant Working Group
- PMID: 39009897
- PMCID: PMC11461624
- DOI: 10.1007/s12072-024-10703-4
Immunosuppression in adult liver transplant recipients: a 2024 update from the Italian Liver Transplant Working Group
Erratum in
-
Correction: Immunosuppression in adult liver transplant recipients: a 2024 update from the Italian Liver Transplant Working Group.Hepatol Int. 2025 Aug;19(4):978-987. doi: 10.1007/s12072-024-10766-3. Hepatol Int. 2025. PMID: 39960604 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: Advances in surgical procedures and immunosuppressive therapies have considerably improved the outcomes of patients who have undergone liver transplantation in the past few decades. In 2020, the Italian Liver Transplant Working Group published practice-oriented algorithms for immunosuppressive therapy (IT) in adult liver transplant (LT) recipients. Due to the rapidly evolving LT field, regular updates to the recommendations are required. This review presents a consensus- and evidence-based update of the 2020 recommendations.
Methods: The Italian Liver Transplant Working Group set out to address new IT issues, which were discussed based on supporting literature and the specialists' personal experiences. The panel deliberated on and graded each statement before consensus was reached.
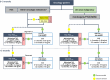
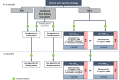
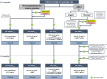
Results: A series of consensus statements were formulated and finalized on: (i) oncologic indications for LT; (ii) management of chronic LT rejection; (iii) combined liver-kidney transplantation; (iv) immunosuppression for transplantation with an organ donated after circulatory death; (v) transplantation in the presence of frailty and sarcopenia; and (vi) ABO blood group incompatibility between donor and recipient. Algorithms were updated in the following LT groups: standard patients, critical patients, oncology patients, patients with specific etiology, and patients at high immunologic risk. A steroid-free approach was generally recommended, except for patients with autoimmune liver disease and those at high immunologic risk.
Conclusion: The updated consensus- and evidence-based 2024 recommendations for immunosuppression regimens in adult patients with ABO-compatible LT address a range of clinical variables that should be considered to optimize the choice of the immunosuppression treatment in clinical practice in Italy.
Keywords: Calcineurin; Hepatocellular cancer; Immunosuppression; Liver metastasis; Liver transplantation; Nephrotoxicity; Recurrence; Rejection; mTOR inhibitor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Tommaso Maria Manzia, Barbara Antonelli, Amedeo Carraro, Grazia Conte, Nicola Guglielmo, Andrea Lauterio, Laura Mameli, Umberto Cillo, Luciano De Carlis, Giuseppe Tisone, Riccardo Volpes, and Massimo Del Gaudio have no conflicts of interest. Paolo De Simone has served as an advisory board member for Novartis, Astellas, and Chiesi. Stefano Fagiuoli is on the Advisory Board and Speaker’s Bureau for AbbVie, Gilead Sciences, MSD, Novartis, Astellas, Bayer, Kedrion, and Intercept. Francesco Lupo served as an advisory board member for Novartis, Astellas, Biotest, and Chiesi.
Figures

References
-
- Karolin A, Genitsch V, Sidler D. Calcineurin inhibitor toxicity in solid organ transplantation. Pharmacology. 2021;106:347–355 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

