Increased susceptibility to kainate-induced seizures in a mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex: Importance of sex and circadian cycle
- PMID: 39010669
- PMCID: PMC11450656
- DOI: 10.1002/epi4.12955
Increased susceptibility to kainate-induced seizures in a mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex: Importance of sex and circadian cycle
Abstract
Objective: Comorbidity of epilepsy and autism in tuberous sclerosis complex 2 (TSC2) is very frequent, but the link between these conditions is still poorly understood. To study neurological problems related to autism, the scientific community has been using an animal model of TSC2, Tsc2+/- mice. However, it is still unknown whether this model has the propensity to exhibit increased seizure susceptibility. Further, the importance of sex and/or the circadian cycle in this biological process has never been addressed. This research aimed to determine whether male and female Tsc2+/- mice have altered seizure susceptibility at light and dark phases.
Methods: We assessed seizure susceptibility and progression in a Tsc2+/- mouse model using the chemical convulsant kainic acid (KA), a potent agonist of the AMPA/kainate class of glutamate receptors. Both male and female animals at adult age were evaluated during non-active and active periods. Seizure severity was determined by integrating individual scores per mouse according to a modified Racine scale. Locomotor behavior was monitored during control and after KA administration.
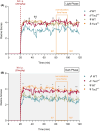
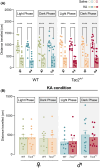
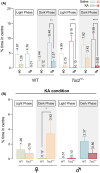
Results: We found increased seizure susceptibility in Tsc2+/- mice with a significant influence of sex and circadian cycle on seizure onset, progression, and behavioral outcomes. While, compared to controls, Tsc2+/- males overall exhibited higher susceptibility independently of circadian cycle, Tsc2+/- females were more susceptible during the dark and post-ovulatory phase. Interestingly, sexual dimorphisms related to KA susceptibility were always reported during light phase independently of the genetic background, with females being the most vulnerable.
Significance: The enhanced susceptibility in the Tsc2 mouse model suggests that other neurological alterations, beside brain lesions, may be involved in seizure occurrence for TSC. Importantly, our work highlighted the importance of considering biological sex and circadian cycle for further studies of TSC-related epilepsy research.
Plain language summary: Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is a rare genetic disorder. It causes brain lesions and is linked to epilepsy, intellectual disability, and autism. We wanted to investigate epilepsy in this model. We found that these mice have more induced seizures than control animals. Our results show that these mice can be used in future epilepsy research for this disorder. We also found that sex and time of day can influence the results. This must be considered in this type of research.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder; biological sex; circadian cycle; epilepsy; tuberous sclerosis complex.
© 2024 The Authors. Epilepsia Open published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International League Against Epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflict of interest. We confirm that we have read the Journal's position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Electro-clinical and neurodevelopmental outcome in six children with early diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis complex and role of the genetic background.Ital J Pediatr. 2020 Mar 27;46(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s13052-020-0801-0. Ital J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32216820 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Selective Effects on Behavior in a Mouse Model of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex.eNeuro. 2020 Apr 29;7(2):ENEURO.0379-19.2020. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0379-19.2020. Print 2020 Mar/Apr. eNeuro. 2020. PMID: 32303566 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Gene Mutation on Seizures in Surgery for Tuberous Sclerosis Complex.Can J Neurol Sci. 2021 May;48(3):327-334. doi: 10.1017/cjn.2020.185. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Can J Neurol Sci. 2021. PMID: 32854808
-
Brain Symptoms of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex: Pathogenesis and Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 22;22(13):6677. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136677. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34206526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A circuitry and biochemical basis for tuberous sclerosis symptoms: from epilepsy to neurocognitive deficits.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013 Nov;31(7):667-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2013.02.008. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23485365 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The hidden rhythms of epilepsy: exploring biological clocks and epileptic seizure dynamics.Acta Epileptol. 2025 Jan 3;7(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s42494-024-00197-w. Acta Epileptol. 2025. PMID: 40217344 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

