ROS induced pyroptosis in inflammatory disease and cancer
- PMID: 39011036
- PMCID: PMC11246884
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1378990
ROS induced pyroptosis in inflammatory disease and cancer
Abstract
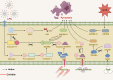
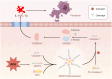
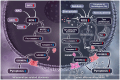
Pyroptosis, a form of caspase-1-dependent cell death, also known as inflammation-dependent death, plays a crucial role in diseases such as stroke, heart disease, or tumors. Since its elucidation, pyroptosis has attracted widespread attention from various sectors. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) can regulate numerous cellular signaling pathways. Through further research on ROS and pyroptosis, the level of ROS has been revealed to be pivotal for the occurrence of pyroptosis, establishing a close relationship between the two. This review primarily focuses on the molecular mechanisms of ROS and pyroptosis in tumors and inflammatory diseases, exploring key proteins that may serve as drug targets linking ROS and pyroptosis and emerging fields targeting pyroptosis. Additionally, the potential future development of compounds and proteins that influence ROS-regulated cell pyroptosis is anticipated, aiming to provide insights for the development of anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Keywords: ROS; cell death; inflammation; pyroptosis; tumor.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Wu, Zhu, Zhao and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

