This is a preprint.
Calibrated CAR Signaling Enables Low-Dose Therapy in Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- PMID: 39011120
- PMCID: PMC11247921
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4619285/v1
Calibrated CAR Signaling Enables Low-Dose Therapy in Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
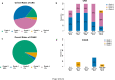
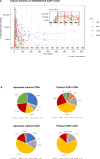
We designed a CD19-targeted CAR comprising a calibrated signaling module, termed 1XX, that differs from that of conventional CD28/CD3z and 4-1BB/CD3z CARs. Here we report the first-in-human, phase 1 clinical trial of 19(T2)28z-1XX CAR T cells in relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma. We hypothesized that 1XX CAR T cells may be effective at low doses and investigated 4 doubling dose levels starting from 25×106 CAR T cells. The overall response rate (ORR) was 82% and complete response (CR) rate 71% in the entire cohort (n=28) and 88% ORR and 75% CR in 16 patients treated at 25×106. With the median follow-up of 24 months, the 1-year EFS was 61% (95% CI: 45-82%). Overall, grade ≥3 CRS and ICANS rates were low at 4% and 7%. The calibrated potency of the 1XX CAR affords excellent efficacy at low cell doses and may benefit the treatment of other hematological malignancies, solid tumors and autoimmunity.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests J.H.P. received consulting fees from Affyimmune Therapeutics, Amgen, Autolus, Be Biopharma, Beigene, Bright Pharmaceutical Services, Inc., Caribou Biosciences, Curocell, Galapagos, In8Bio, Kite, Medpace, Minerva Biotechnologies, Pfizer, Servier, Sobi, and Takeda; received honoraria from OncLive, Physician Education Resource, and MJH Life Sciences; serves on scientific advisory board of Allogene Therapeutics, Artiva Biotherapeutics and Green Cross Biopharma; and received institutional research funding from Autolus, Genentech, Fate Therapeutics, InCyte, Servier, and Takeda. M.L.P. received consulting fees from BMS, Cellectis, Kite, Mustang Bio and Synthekine. G.Sh. received research funding to the institution from Amgen, BMS, Beyond Spring, Janssen, and GPCR, and serves on DSMB for Arcellx. P.D. received consulting fees from Kite. M.Sc. served as a paid consultant for McKinsey & Company, Angiocrine Bioscience, Inc., Kite, and Omeros Corporation; received research funding from Angiocrine Bioscience, Inc., Omeros Corporation, and Amgen, Inc.; served on ad hoc advisory boards for Kite-A Gilead company; and received honoraria from i3Health, Medscape and CancerNetwork for CME-related activity. G.Sa. has received financial compensations for participating in advisory boards or consulting for Abbvie, Atbtherapeutics, Beigene, BMS, Debiopharm Genentech/Roche, Genmab, Incyte, Ipsen, Janssen, Kite/Gilead, Loxo/Lilly, Merck, Molecular Partners, Nordic Nanovector, Novartis, Nurix and Orna. He is also a shareholder of: Owkin; he received Research Support managed by his institution from Genentech, Janssen, Ipsen, Nurix. Y.K.V. received one time consulting fee from EastRx. J.M.S. is an inventor on 1XX related IP. I.R. reports grants from Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Atara, personal fees from Mnemo Therapeutics, Akron, the Centre for Commercialization of Cancer, and Oribiotech, and other support from Bristol Myers Squibb outside the submitted work. M. S. reports grants from Atara Biotherapeutics outside the submitted work, as well as patent 8389282 issued and licensed to Juno Therapeutics, patent 11242375 issued and licensed to Atara Biotherapeutics, patent 10370452 issued, licensed, and with royalties paid from Fate Therapeutics, patent 11377637 issued and licensed to Takeda Pharmaceuticals, patent 11377637 issued and licensed to Mnemo Therapeutics, and patent 11377637 issued and licensed to Minerva Biotechnologies. MSK has licensed 1XX technology to Atara Biotherapy, Fate Therapeutics, Minerva Therapeutics, and Takeda Pharmaceuticals.
Figures


References
-
- Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon LI, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet (London, England) 2020;396(10254):839–852. (In eng). DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31366-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

