Prepandemic Metabolic Correlates of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Severity and Long COVID Incidence in People Living With HIV
- PMID: 39011957
- PMCID: PMC12102488
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiae362
Prepandemic Metabolic Correlates of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Severity and Long COVID Incidence in People Living With HIV
Abstract
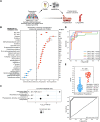
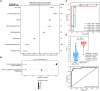
Host metabolic dysregulation, especially in tryptophan metabolism, is intricately linked to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity and its postacute sequelae (long COVID). People living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV; PLWH) experience similar metabolic dysregulation and face an increased risk of developing long COVID. However, whether preexisting HIV-associated metabolic dysregulations contribute in predisposing PLWH to severe COVID-19 outcomes remains underexplored. Analyzing prepandemic samples from PLWH with documented postinfection outcomes, we found specific metabolic alterations, including increased tryptophan catabolism, predicting an elevated risk of severe COVID-19 and the incidence of long COVID. These alterations warrant further investigation for their potential prognostic and mechanistic significance in determining COVID-19 complications.
Keywords: COVID-19; HIV; long COVID; metabolites; tryptophan.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For commercial re-use, please contact reprints@oup.com for reprints and translation rights for reprints. All other permissions can be obtained through our RightsLink service via the Permissions link on the article page on our site—for further information please contact journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors: No reported conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI037984/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AA029859/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG062383/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK123733/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA010815/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146208/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001409/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146192/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR001431/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI 045008 to/Penn Center for AIDS Research
- U01 HL146193/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS117458/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- TUHS Auxiliary Endowment for Excellence
- R01 AI165079/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146194/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146241/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050409/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146333/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA029859/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AI157875/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146245/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD023586/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH116867/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR001432/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011104/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI045008/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1UM1Al126620/to Cure HIV-1 Infection by Combination Immunotherapy
- R24 AA026801/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146242/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI073961/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146201/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI170166/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- BEAT-HIV Martin Delaney Collaboratory
- U01 HL146204/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- American Lung Association
- at TNRPC
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146240/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146203/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003098/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

