Bipotential B-neutrophil progenitors are present in human and mouse bone marrow and emerge in the periphery upon stress hematopoiesis
- PMID: 39012145
- PMCID: PMC11323571
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.01599-24
Bipotential B-neutrophil progenitors are present in human and mouse bone marrow and emerge in the periphery upon stress hematopoiesis
Abstract
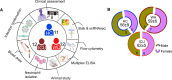
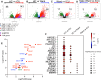
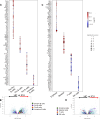
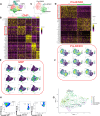
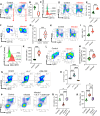
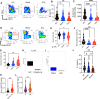
Hematopoiesis is a tightly regulated process that gets skewed toward myelopoiesis. This restrains lymphopoiesis, but the role of lymphocytes in this process is not well defined. To unravel the intricacies of neutrophil responses in COVID-19, we performed bulk RNAseq on neutrophils from healthy controls and COVID-19 patients. Principal component analysis revealed distinguishing neutrophil gene expression alterations in COVID-19 patients. ICU and ward patients displayed substantial transcriptional changes, with ICU patients exhibiting a more pronounced response. Intriguingly, neutrophils from COVID-19 patients, notably ICU patients, exhibited an enrichment of immunoglobulin (Ig) and B cell lineage-associated genes, suggesting potential lineage plasticity. We validated our RNAseq findings in a larger cohort. Moreover, by reanalyzing single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) data on human bone marrow (BM) granulocytes, we identified the cluster of granulocyte-monocyte progenitors (GMP) enriched with Ig and B cell lineage-associated genes. These cells with lineage plasticity may serve as a resource depending on the host's needs during severe systemic infection. This distinct B cell subset may play a pivotal role in promoting myelopoiesis in response to infection. The scRNAseq analysis of BM neutrophils in infected mice further supported our observations in humans. Finally, our studies using an animal model of acute infection implicate IL-7/GM-CSF in influencing neutrophil and B cell dynamics. Elevated GM-CSF and reduced IL-7 receptor expression in COVID-19 patients imply altered hematopoiesis favoring myeloid cells over B cells. Our findings provide novel insights into the relationship between the B-neutrophil lineages during severe infection, hinting at potential implications for disease pathogenesis.
Importance: This study investigates the dynamics of hematopoiesis in COVID-19, focusing on neutrophil responses. Through RNA sequencing of neutrophils from healthy controls and COVID-19 patients, distinct gene expression alterations are identified, particularly in ICU patients. Notably, neutrophils from COVID-19 patients, especially in the ICU, exhibit enrichment of immunoglobulin and B cell lineage-associated genes, suggesting potential lineage plasticity. Validation in a larger patient cohort and single-cell analysis of bone marrow granulocytes support the presence of granulocyte-monocyte progenitors with B cell lineage-associated genes. The findings propose a link between B-neutrophil lineages during severe infection, implicating a potential role for these cells in altered hematopoiesis favoring myeloid cells over B cells. Elevated GM-CSF and reduced IL-7 receptor expression in stress hematopoiesis suggest cytokine involvement in these dynamics, providing novel insights into disease pathogenesis.
Keywords: GM-CSF; IL-7; Pre B cell; Pro B cell; hybrid cells; myeloid plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
