Dysphagia in primary progressive aphasia: Clinical predictors and neuroanatomical basis
- PMID: 39012305
- PMCID: PMC11295169
- DOI: 10.1111/ene.16370
Dysphagia in primary progressive aphasia: Clinical predictors and neuroanatomical basis
Abstract
Background and purpose: Dysphagia is an important feature of neurodegenerative diseases and potentially life-threatening in primary progressive aphasia (PPA) but remains poorly characterized in these syndromes. We hypothesized that dysphagia would be more prevalent in nonfluent/agrammatic variant (nfv)PPA than other PPA syndromes, predicted by accompanying motor features, and associated with atrophy affecting regions implicated in swallowing control.
Methods: In a retrospective case-control study at our tertiary referral centre, we recruited 56 patients with PPA (21 nfvPPA, 22 semantic variant [sv]PPA, 13 logopenic variant [lv]PPA). Using a pro forma based on caregiver surveys and clinical records, we documented dysphagia (present/absent) and associated, potentially predictive clinical, cognitive, and behavioural features. These were used to train a machine learning model. Patients' brain magnetic resonance imaging scans were assessed using voxel-based morphometry and region-of-interest analyses comparing differential atrophy profiles associated with dysphagia presence/absence.
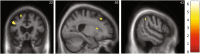
Results: Dysphagia was significantly more prevalent in nfvPPA (43% vs. 5% svPPA and no lvPPA). The machine learning model revealed a hierarchy of features predicting dysphagia in the nfvPPA group, with excellent classification accuracy (90.5%, 95% confidence interval = 77.9-100); the strongest predictor was orofacial apraxia, followed by older age, parkinsonism, more severe behavioural disturbance, and more severe cognitive impairment. Significant grey matter atrophy correlates of dysphagia in nfvPPA were identified in left middle frontal, right superior frontal, and right supramarginal gyri and right caudate.
Conclusions: Dysphagia is a common feature of nfvPPA, linked to underlying corticosubcortical network dysfunction. Clinicians should anticipate this symptom particularly in the context of other motor features and more severe disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer dementia; dysphagia; primary progressive aphasia; semantic dementia; swallowing.
© 2024 The Author(s). European Journal of Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hardy CJD, Taylor‐Rubin C, Taylor B, et al. Symptom‐led staging for primary progressive aphasia [Internet]. 2023; 2023.03.13.23286972 [cited 2023 Mar 22]. Available from: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.03.13.23286972v1 - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- ALZS_/Alzheimer's Society/United Kingdom
- 204841/Z/16/Z/The National Brain Appeal Royal National Institute for Deaf People (Discovery Grant G105_WARREN)National Institute for Health Research University College London Hospitals Biomedical Research Centre NIHR Advanced Fellowship NIHR302240 UKRI and Wellcome Trust
- National Brain Appeal
- NIHR204280/Invention for Innovation
- 204841/Z/16/Z/Wellcome Institutional Strategic Support Fund Award
- Miriam Marks Brain Research UK Senior Fellowship
- MR/M008525/1/Medical Research Council Clinician Scientist Fellowship
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- Alzheimer's Research UK
- BRC149/NS/MH/National Institute for Health Research Rare Disease Translational Research Collaboration
- UK Dementia Research Institute
- Association of British Neurologists Clinical Research Training Fellowship
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

