Neuroepigenetic Editing
- PMID: 39012593
- PMCID: PMC11520296
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4051-7_6
Neuroepigenetic Editing
Abstract
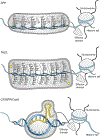
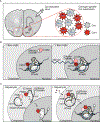
Epigenetic regulation is intrinsic to basic neurobiological function as well as neurological disease. Regulation of chromatin-modifying enzymes in the brain is critical during both development and adulthood and in response to external stimuli. Biochemical studies are complemented by numerous next-generation sequencing (NGS) studies that quantify global changes in gene expression, chromatin accessibility, histone and DNA modifications in neurons and glial cells. Neuroepigenetic editing tools are essential to distinguish between the mere presence and functional relevance of histone and DNA modifications to gene transcription in the brain and animal behavior. This review discusses current advances in neuroepigenetic editing, highlighting methodological considerations pertinent to neuroscience, such as delivery methods and the spatiotemporal specificity of editing and it demonstrates the enormous potential of epigenetic editing for basic neurobiological research and therapeutic application.
Keywords: Epigenetic editing; chromatin; neuroscience; psychiatric disease.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Figures
References
-
- Allis CD, Jenuwein T (2016) The molecular hallmarks of epigenetic control. Nat Rev Genet 17 - PubMed
-
- Smith ZD, Meissner A (2013) DNA methylation: Roles in mammalian development. Nat Rev Genet 14 - PubMed
-
- Meaney MJ (2013) Epigenetics and the environmental regulation of the genome and its function. In: Evolution, early experience and human development: from research to practice and policy, pp 439–466
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

