Surface properties of the seas of Titan as revealed by Cassini mission bistatic radar experiments
- PMID: 39013844
- PMCID: PMC11252143
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49837-2
Surface properties of the seas of Titan as revealed by Cassini mission bistatic radar experiments
Abstract
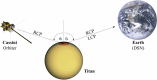
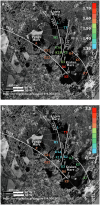
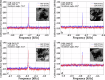
Saturn's moon Titan was explored by the Cassini spacecraft from 2004 to 2017. While Cassini revealed a lot about this Earth-like world, its radar observations could only provide limited information about Titan's liquid hydrocarbons seas Kraken, Ligeia and Punga Mare. Here, we show the results of the analysis of the Cassini mission bistatic radar experiments data of Titan's polar seas. The dual-polarized nature of bistatic radar observations allow independent estimates of effective relative dielectric constant and small-scale roughness of sea surface, which were not possible via monostatic radar data. We find statistically significant variations in effective dielectric constant (i.e., liquid composition), consistent with a latitudinal dependence in the methane-ethane mixing-ratio. The results on estuaries suggest lower values than the open seas, compatible with methane-rich rivers entering seas with higher ethane content. We estimate small-scale roughness of a few millimeters from the almost purely coherent scattering from the sea surface, hinting at the presence of capillary waves. This roughness is concentrated near estuaries and inter-basin straits, perhaps indicating active tidal currents.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lopes RMC, et al. Space Sci. Rev. 2019;215:33. doi: 10.1007/s11214-019-0598-6. - DOI
-
- Hayes AG. The lakes and seas of Titan. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2016;44:57–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-060115-012247. - DOI
-
- Hayes AG, Lorenz RD, Lunine JI. A post-Cassini view of Titan’s methane-based hydrologic cycle. Nat. Geosci. 2018;11:306–313. doi: 10.1038/s41561-018-0103-y. - DOI
-
- Mitchell JL, Lora JM. The climate of Titan. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2016;44:353–380. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-060115-012428. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

