Continuous blood pressure prediction system using Conv-LSTM network on hybrid latent features of photoplethysmogram (PPG) and electrocardiogram (ECG) signals
- PMID: 39014018
- PMCID: PMC11252121
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66514-y
Continuous blood pressure prediction system using Conv-LSTM network on hybrid latent features of photoplethysmogram (PPG) and electrocardiogram (ECG) signals
Abstract
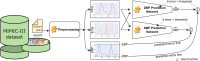
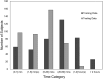
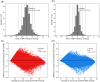
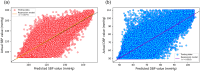
Continuous blood pressure (BP) monitoring is essential for managing cardiovascular disease. However, existing devices often require expert handling, highlighting the need for alternative methods to simplify the process. Researchers have developed various methods using physiological signals to address this issue. Yet, many of these methods either fall short in accuracy according to the BHS, AAMI, and IEEE standards for BP measurement devices or suffer from low computational efficiency due to the complexity of their models. To solve this problem, we developed a BP prediction system that merges extracted features of PPG and ECG from two pulses of both signals using convolutional and LSTM layers, followed by incorporating the R-to-R interval durations as additional features for predicting systolic (SBP) and diastolic (DBP) blood pressure. Our findings indicate that the prediction accuracies for SBP and DBP were 5.306 ± 7.248 mmHg with a 0.877 correlation coefficient and 3.296 ± 4.764 mmHg with a 0.918 correlation coefficient, respectively. We found that our proposed model achieved a robust performance on the MIMIC III dataset with a minimum architectural design and high-level accuracy compared to existing methods. Thus, our method not only meets the passing category for BHS, AAMI, and IEEE guidelines but also stands out as the most rapidly accurate deep-learning-based BP measurement device currently available.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Deep learning; Electrocardiography; LSTM; Photoplethysmography.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Hager, H. H. & Burns, B. Artery cannulation. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls publishing; -Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482242/ - PubMed
-
- Bote JM, Recas J, Hermida R. Evaluation of blood pressure estimation models based on pulse arrival time. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2020;84:106616. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2020.106616. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

