Temporal changes in CT-derived fractional flow reserve in patients after heart transplantation
- PMID: 39014089
- PMCID: PMC11631993
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-024-10932-z
Temporal changes in CT-derived fractional flow reserve in patients after heart transplantation
Abstract
Background: Adding functional information by CT-derived fractional flow reserve (FFRct) to coronary CT angiography (CCTA) and assessing its temporal change may provide insight into the natural history and physiopathology of cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) in heart transplantation (HTx) patients. We assessed FFRct changes as well as CAV progression over a 2-year period in HTx patients undergoing serial CT imaging.
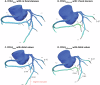
Methods: HTx patients from Erasmus MC and Mount Sinai Hospital, who had consecutive CCTAs 2 years apart were evaluated. FFRct analysis was performed for both scans. FFRct values at the most distal point in the left anterior descending (LAD), left circumflex (LCX), and right coronary artery (RCA) were measured after precisely matching the anatomical locations in both analyses. Also, the number of anatomical coronary stenoses of > 30% was scored.
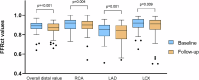
Results: In total, 106 patients (median age 57 [interquartile range 47-67] years, 67% male) at 9 [6-13] years after HTx at the time of the baseline CCTA were included. Median distal FFRct values significantly decreased from baseline to follow-up for the LAD from 0.85 [0.79-0.90] to 0.84 [0.76-0.90] (p = 0.001), LCX from 0.92 [0.88-0.96] to 0.91 [0.85-0.95] (p = 0.009), and RCA from 0.92 [0.86-0.95] to 0.90 [0.86-0.94] (p = 0.004). The number of focal anatomical stenoses of > 30% increased from a median of 1 [0-2] at baseline to 2 [0-3] at follow-up (p = 0.009).
Conclusions: The distal coronary FFRct values in post-HTX patients in each of the three major coronary arteries decreased, and the number of focal coronary stenoses increased over a 2-year period. Temporal FFRct change rate may become an additional parameter in the follow-up of HTx patients, but more research is needed to elucidate its role.
Clinical relevance statement: CT-derived fractional flow reserve (FFRct) is important post-heart transplant because of additional information on coronary CT angiography for cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) detection. The decrease and degree of reduction in distal FFRct value may indicate progression in anatomic CAV burden.
Key points: CT-derived fractional flow reserve (FFRct) is important for monitoring cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) in heart transplant patients. Over time, transplant patients showed a decrease in distal FFRct and an increase in coronary stenoses. Temporal changes in FFRct could be crucial for transplant follow-up, aiding in CAV detection.
Keywords: Computed tomography angiography; Fractional flow reserve; Heart transplantation; Myocardial.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standards. Guarantor: The scientific guarantors of this publication are Prof. R.P.J. Budde and Dr. O.C. Manintveld. Conflict of interest: S.P.S.: no conflict of interest. J.S.: no conflict of interest. A.H.: received a research grant and consultancy fees from GE Healthcare and speaker fees from GE Healthcare and Bayer. He is also a member of the medical advisory board of Medis Medical Imaging Systems and was the MRI corelab supervisor of Cardialysis BV until 2022. R.P.: no conflict of interest. A.A.C.: no conflict of interest. M.B.: no conflict of interest. D.M.M.: no conflict of interest. J.J.B.: Dr. Brugts received an independent research grant for ISS to the hospital. Dr. Brugts has had speaker engagements or advisory boards in the past 5 years with Astra Zeneca, Abbott, Bayer, Boehringer, Danchii Sankyo, Novartis and Vifor. K.C.: no conflict of interest. Y.J.H.J.T.: no conflict of interest. O.M.: reports personal fees from Astra Zeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sanyo and Novartis. R.P.J.B.: Institutional support to Erasmus MC from Siemens Healthineers; lecture fee and travel reimbursement from Siemens Healthineers paid directly to Erasmus MC; lecture fee from Bayer; board member of the European Society of Cardiovascular Radiology and the Cardiovascular section of the Dutch Society of Radiology; editorial board member of Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, European Heart Journal—Digital Health, and the European Journal of Hybrid Imaging; grant from HeartFlow to Erasmus MC. Statistics and biometry: Dr. A. Hirsch kindly provided statistical advice for this manuscript. One of the authors has significant statistical expertise. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Informed consent: Only if the study is on human subjects: written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Ethical approval: Institutional Review Board approval was obtained. Study subjects or cohorts overlap: Some study subjects or cohorts have been previously reported in ref. [16]. Methodology: Retrospective Observational Multicenter study
Figures
References
-
- ISHLT (2018) Adult Heart Transplantation Statistics 2018 slides ISHLT. Available via https://ishltregistries.org/registries/slides.asp?yearToDisplay=2018. Accessed 10 Aug 2022
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

