NTRK-fused central nervous system tumours: clinicopathological and genetic insights and response to TRK inhibitors
- PMID: 39014476
- PMCID: PMC11251294
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-024-01798-9
NTRK-fused central nervous system tumours: clinicopathological and genetic insights and response to TRK inhibitors
Abstract
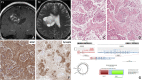
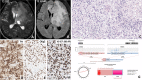
Background Neurotrophic tropomyosin receptor kinase (NTRK) gene fusions are found in 1% of gliomas across children and adults. TRK inhibitors are promising therapeutic agents for NTRK-fused gliomas because they are tissue agnostic and cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Methods We investigated twelve NGS-verified NTRK-fused gliomas from a single institute, Seoul National University Hospital. Results The patient cohort included six children (aged 1-15 years) and six adults (aged 27-72 years). NTRK2 fusions were found in ten cerebral diffuse low-grade and high-grade gliomas (DLGGs and DHGGs, respectively), and NTRK1 fusions were found in one cerebral desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma and one spinal DHGG. In this series, the fusion partners of NTRK2 were HOOK3, KIF5A, GKAP1, LHFPL3, SLMAP, ZBTB43, SPECC1L, FKBP15, KANK1, and BCR, while the NTRK1 fusion partners were TPR and TPM3. DLGGs tended to harbour only an NTRK fusion, while DHGGs exhibited further genetic alterations, such as TERT promoter/TP53/PTEN mutation, CDKN2A/2B homozygous deletion, PDGFRA/KIT/MDM4/AKT3 amplification, or multiple chromosomal copy number aberrations. Four patients received adjuvant TRK inhibitor therapy (larotrectinib, repotrectinib, or entrectinib), among which three also received chemotherapy (n = 2) or proton therapy (n = 1). The treatment outcomes for patients receiving TRK inhibitors varied: one child who received larotrectinib for residual DLGG maintained stable disease. In contrast, another child with DHGG in the spinal cord experienced multiple instances of tumour recurrence. Despite treatment with larotrectinib, ultimately, the child died as a result of tumour progression. An adult patient with glioblastoma (GBM) treated with entrectinib also experienced tumour progression and eventually died. However, there was a successful outcome for a paediatric patient with DHGG who, after a second gross total tumour removal followed by repotrectinib treatment, showed no evidence of disease. This patient had previously experienced relapse after the initial surgery and underwent autologous peripheral blood stem cell therapy with carboplatin/thiotepa and proton therapy. Conclusions Our study clarifies the distinct differences in the pathology and TRK inhibitor response between LGG and HGG with NTRK fusions.
Keywords: NTRK fusion; Brain tumours; Next-generation sequencing; TRK inhibitors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bourhis A, Caumont C, Quintin-Roue I, Magro E, Dissaux G, Remoue A, Le Noac'h P, Douet-Guilbert N, Seizeur R, Tyulyandina A, et al. Detection of NTRK fusions in glioblastoma: fluorescent in situ hybridisation is more useful than pan-TRK immunohistochemistry as a screening tool prior to RNA sequencing. Pathology. 2022;54:55–62. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2021.05.100. - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Carvalho C, Correa D, Tesser-Gamba F, Dias Oliveira I, Saba da Silva N, Capellano AM, de Seixas Alves MT, Dastoli PA, Cavalheiro S, Caminada de Toledo SR. Gliomas in children and adolescents: investigation of molecular alterations with a potential prognostic and therapeutic impact. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022;148:107–119. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03813-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Winne K, Sorber L, Lambin S, Siozopoulou V, Beniuga G, Dedeurwaerdere F, D'Haene N, Habran L, Libbrecht L, Van Huysse J, et al. Immunohistochemistry as a screening tool for NTRK gene fusions: results of a first Belgian ring trial. Virchows Arch. 2021;478:283–291. doi: 10.1007/s00428-020-02921-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doebele RC, Drilon A, Paz-Ares L, Siena S, Shaw AT, Farago AF, Blakely CM, Seto T, Cho BC, Tosi D, et al. Entrectinib in patients with advanced or metastatic NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours: integrated analysis of three phase 1–2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:271–282. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30691-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

