PARK7/DJ-1 deficiency impairs microglial activation in response to LPS-induced inflammation
- PMID: 39014482
- PMCID: PMC11253405
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-024-03164-x
PARK7/DJ-1 deficiency impairs microglial activation in response to LPS-induced inflammation
Abstract
Background: Specific microglia responses are thought to contribute to the development and progression of neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson's disease (PD). However, the phenotypic acquisition of microglial cells and their role during the underlying neuroinflammatory processes remain largely elusive. Here, according to the multiple-hit hypothesis, which stipulates that PD etiology is determined by a combination of genetics and various environmental risk factors, we investigate microglial transcriptional programs and morphological adaptations under PARK7/DJ-1 deficiency, a genetic cause of PD, during lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation.
Methods: Using a combination of single-cell RNA-sequencing, bulk RNA-sequencing, multicolor flow cytometry and immunofluorescence analyses, we comprehensively compared microglial cell phenotypic characteristics in PARK7/DJ-1 knock-out (KO) with wildtype littermate mice following 6- or 24-h intraperitoneal injection with LPS. For translational perspectives, we conducted corresponding analyses in human PARK7/DJ-1 mutant induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived microglia and murine bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs).
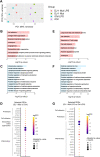
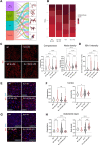
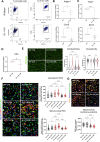
Results: By excluding the contribution of other immune brain resident and peripheral cells, we show that microglia acutely isolated from PARK7/DJ-1 KO mice display a distinct phenotype, specially related to type II interferon and DNA damage response signaling, when compared with wildtype microglia, in response to LPS. We also detected discrete signatures in human PARK7/DJ-1 mutant iPSC-derived microglia and BMDMs from PARK7/DJ-1 KO mice. These specific transcriptional signatures were reflected at the morphological level, with microglia in LPS-treated PARK7/DJ-1 KO mice showing a less amoeboid cell shape compared to wildtype mice, both at 6 and 24 h after acute inflammation, as also observed in BMDMs.
Conclusions: Taken together, our results show that, under inflammatory conditions, PARK7/DJ-1 deficiency skews microglia towards a distinct phenotype characterized by downregulation of genes involved in type II interferon signaling and a less prominent amoeboid morphology compared to wildtype microglia. These findings suggest that the underlying oxidative stress associated with the lack of PARK7/DJ-1 affects microglia neuroinflammatory responses, which may play a causative role in PD onset and progression.
Keywords: PARK7/DJ-1; Lipopolysaccharide; Microglia; Microglia morphology; Neuroinflammation; Parkinson’s disease.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Amatullah H, Shan Y, Beauchamp BL, Gali PL, Gupta S, Maron-Gutierrez T, Speck ER, Fox-Robichaud AE, Tsang JL, Mei SH, Mak TW, Rocco PR, Semple JW, Zhang H, Hu P, Marshall JC, Stewart DJ, Harper ME, Liaw PC, Liles WC, Dos Santos CC, G. Canadian Critical Care Translational Biology DJ-1/PARK7 impairs bacterial clearance in sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195(7):889–905. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201604-0730OC. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baumuratov AS, Antony PM, Ostaszewski M, He F, Salamanca L, Antunes L, Weber J, Longhino L, Derkinderen P, Koopman WJ, Diederich NJ. Enteric neurons from Parkinson's disease patients display ex vivo aberrations in mitochondrial structure. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33117. doi: 10.1038/srep33117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bodea LG, Wang Y, Linnartz-Gerlach B, Kopatz J, Sinkkonen L, Musgrove R, Kaoma T, Muller A, Vallar L, Di Monte DA, Balling R, Neumann H. Neurodegeneration by activation of the microglial complement-phagosome pathway. J Neurosci. 2014;34(25):8546–8556. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5002-13.2014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PRIDE/14254520/I2TRON/Fonds National de la Recherche Luxembourg
- AFR/6916713/Fonds National de la Recherche Luxembourg
- PRIDE/10907093/CRITICS/Fonds National de la Recherche Luxembourg
- C21/BM/15739125/DIOMEDES/Fonds National de la Recherche Luxembourg
- INTER/DFG/17/11583046/Fonds National de la Recherche Luxembourg
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

