H3K27ac acts as a molecular switch for doxorubicin-induced activation of cardiotoxic genes
- PMID: 39014511
- PMCID: PMC11251309
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-024-01709-8
H3K27ac acts as a molecular switch for doxorubicin-induced activation of cardiotoxic genes
Abstract
Background: Doxorubicin (Dox) is an effective chemotherapeutic drug for various cancers, but its clinical application is limited by severe cardiotoxicity. Dox treatment can transcriptionally activate multiple cardiotoxicity-associated genes in cardiomyocytes, the mechanisms underlying this global gene activation remain poorly understood.
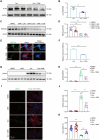
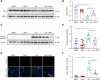
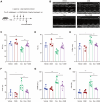
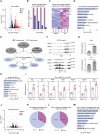
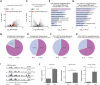
Methods and results: Herein, we integrated data from animal models, CUT&Tag and RNA-seq after Dox treatment, and discovered that the level of H3K27ac (a histone modification associated with gene activation) significantly increased in cardiomyocytes following Dox treatment. C646, an inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase, reversed Dox-induced H3K27ac accumulation in cardiomyocytes, which subsequently prevented the increase of Dox-induced DNA damage and apoptosis. Furthermore, C646 alleviated cardiac dysfunction in Dox-treated mice by restoring ejection fraction and reversing fractional shortening percentages. Additionally, Dox treatment increased H3K27ac deposition at the promoters of multiple cardiotoxic genes including Bax, Fas and Bnip3, resulting in their up-regulation. Moreover, the deposition of H3K27ac at cardiotoxicity-related genes exhibited a broad feature across the genome. Based on the deposition of H3K27ac and mRNA expression levels, several potential genes that might contribute to Dox-induced cardiotoxicity were predicted. Finally, the up-regulation of H3K27ac-regulated cardiotoxic genes upon Dox treatment is conservative across species.
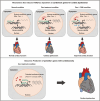
Conclusions: Taken together, Dox-induced epigenetic modification, specifically H3K27ac, acts as a molecular switch for the activation of robust cardiotoxicity-related genes, leading to cardiomyocyte death and cardiac dysfunction. These findings provide new insights into the relationship between Dox-induced cardiotoxicity and epigenetic regulation, and identify H3K27ac as a potential target for the prevention and treatment of Dox-induced cardiotoxicity.
Keywords: Broad H3K27ac; DNA damage; Dox-induced cardiotoxicity; Histone modification.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Yeasmin S, Azharuddin M. Effect of exercise on gait and postural control in patients with chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review. Sport Sci Health. 2024. 10.1007/s11332-024-01168-x
-
- Burstein HJ, Mangu PB, Somerfield MR, Schrag D, Samson D, Holt L, Zelman D, Ajani JA. American society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline update on the use of chemotherapy sensitivity and resistance assays. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(24):3328–3330. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.36.0354. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

