An evaluation of the outcomes associated with peritoneal catheter use in neonates undergoing cardiac surgery: A multicenter study
- PMID: 39015443
- PMCID: PMC11247230
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xjon.2024.03.009
An evaluation of the outcomes associated with peritoneal catheter use in neonates undergoing cardiac surgery: A multicenter study
Abstract
Objective: The study objective was to determine if intraoperative peritoneal catheter placement is associated with improved outcomes in neonates undergoing high-risk cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass.
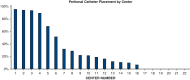
Methods: This propensity score-matched retrospective study used data from 22 academic pediatric cardiac intensive care units. Consecutive neonates undergoing Society of Thoracic Surgeons-European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery category 3 to 5 cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass at centers participating in the NEonatal and Pediatric Heart Renal Outcomes Network collaborative were studied to determine the association of the use of an intraoperative placed peritoneal catheter for dialysis or passive drainage with clinical outcomes, including the duration of mechanical ventilation.
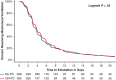
Results: Among 1490 eligible neonates in the NEonatal and Pediatric Heart Renal Outcomes Network dataset, a propensity-matched analysis was used to compare 395 patients with peritoneal catheter placement with 628 patients without peritoneal catheter placement. Time to extubation and most clinical outcomes were similar. Postoperative length of stay was 5 days longer in the peritoneal catheter placement cohort (17 vs 22 days, P = .001). There was a 50% higher incidence of moderate to severe acute kidney injury in the no-peritoneal catheter cohort (12% vs 18%, P = .02). Subgroup analyses between specific treatments and in highest risk patients yielded similar associations.
Conclusions: This study does not demonstrate improved outcomes among neonates with placement of a peritoneal catheter during cardiac surgery. Outcomes were similar apart from longer hospital stay in the peritoneal catheter cohort. The no-peritoneal catheter cohort had a 50% higher incidence of moderate to severe acute kidney injury (12% vs 18%). This analysis does not support indiscriminate peritoneal catheter use, although it may support the utility for postoperative fluid removal among neonates at risk for acute kidney injury. A multicenter controlled trial may better elucidate peritoneal catheter effects.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; fluid overload; neonatal cardiac surgery; peritoneal catheter; peritoneal dialysis.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported no conflicts of interest. The Journal policy requires editors and reviewers to disclose conflicts of interest and to decline handling or reviewing manuscripts for which they may have a conflict of interest. The editors and reviewers of this article have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bellos I., Iliopoulos D.C., Perrea D.N. Association of postoperative fluid overload with adverse outcomes after congenital heart surgery: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Pediatr Nephrol. 2020;35:1109–1119. - PubMed
-
- Mah K.E., Hao S., Sutherland S.M., et al. Fluid overload independent of acute kidney injury predicts poor outcomes in neonates following congenital heart surgery. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018;33:511–520. - PubMed
-
- Akcan-Arikan A., Gebhard D.J., Arnold M.A., Loftis L.L., Kennedy C.E. Fluid overload and kidney injury score: a multidimensional real-time assessment of renal disease burden in the critically ill patient. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2017;18(6):524–530. - PubMed
-
- Piggott K.D., Soni M., Decampli W.M., et al. Acute kidney injury and fluid overload in neonates following surgery for congenital heart disease. World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg. 2015;6(3):401–406. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

