Nomogram for predicting the risk of central lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a combination of sonographic findings and clinical factors
- PMID: 39015718
- PMCID: PMC11247594
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-24-154
Nomogram for predicting the risk of central lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a combination of sonographic findings and clinical factors
Abstract
Background: A considerable controversy over performing thyroidectomy and central lymph node dissection in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC) remained. However, accurate prediction of central lymph node metastasis (CLNM) is crucial for surgical extent and proper management. The aim of this study was to develop and validate a practical nomogram for predicting CLNM in patients with PTMC.
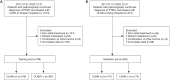
Methods: A total of 1,029 patients with PTMC who underwent thyroidectomy and central lymph node dissection at Tangdu Hospital (the Second Affiliated Hospital of Air Force Medical University) and Xijing Hospital (the First Affiliated Hospital of Air Force Medical University) were selected. Seven hundred and nine patients were assigned to the training set and 320 patients to the validation set. Data encompassing demographic characteristics, ultrasonography results, and biochemical indicators were obtained. Stepwise backward selection and multiple logistic regression were used to screen the variables and establish the nomogram. Concordance index (C-index), receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, and decision curve analysis (DCA) were employed to evaluate the nomogram's distinguishability, accuracy, and clinical utility.
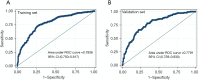
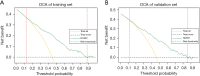
Results: Young age, multifocality, bigger tumor, presence of microcalcification, aspect ratio (height divided by width) ≥1, loss of fatty hilum, high free thyroxine (FT4), and lower anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPOAb) were significantly associated with CLNM. The nomogram showed strong predictive capacity, with a C-index and accuracy of 0.784 and 0.713 in the training set and 0.779 and 0.703 in the external validation set, respectively. DCA indicated that the nomogram demonstrated strong clinical applicability.
Conclusions: We established a reliable, cost-effective, reproducible, and noninvasive nomogram for predicting CLNM in patients with PTMC. This tool could be a valuable guidance for deciding on management in PTMC.
Keywords: Nomogram; central lymph node metastasis (CLNM); microcarcinoma; papillary thyroid cancer (PTC); ultrasonography (US).
2024 Gland Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://gs.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/gs-24-154/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
