miRNA and leptin signaling in metabolic diseases and at extreme environments
- PMID: 39017237
- PMCID: PMC11253706
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.1248
miRNA and leptin signaling in metabolic diseases and at extreme environments
Abstract
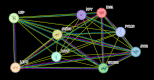
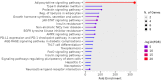
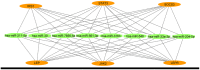
The burden of growing concern about the dysregulation of metabolic processes arises due to complex interplay between environment and nutrition that has great impact on genetics and epigenetics of an individual. Thereby, any abnormality at the level of food intake regulating hormones may contribute to the development of metabolic diseases in any age group due to malnutrition, overweight, changing lifestyle, and exposure to extreme environments such as heat stress (HS), cold stress, or high altitude (HA). Hormones such as leptin, adiponectin, ghrelin, and cholecystokinin regulate appetite and satiety to maintain energy homeostasis. Leptin, an adipokine and a pleiotropic hormone, play major role in regulating the food intake, energy gain and energy expenditure. Using in silico approach, we have identified the major genes (LEP, LEPR, JAK2, STAT3, NPY, POMC, IRS1, SOCS3) that play crucial role in leptin signaling pathway. Further, eight miRNAs (hsa-miR-204-5p, hsa-miR-211-5p, hsa-miR-30, hsa-miR-3163, hsa-miR-33a-3p, hsa-miR-548, hsa-miR-561-3p, hsa-miR-7856-5p) from TargetScan 8.0 database were screened out that commonly target these genes. The role of these miRNAs should be explored as they might play vital role in regulating the appetite, energy metabolism, metabolic diseases (obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, inflammation), and to combat extreme environments. The miRNAs regulating leptin signaling and appetite may be useful for developing novel therapeutics for metabolic diseases.
Keywords: appetite; high altitude; leptin; metabolic diseases; microRNA.
© 2024 The Author(s). Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
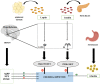
 represents inhibition; and
represents inhibition; and  represents stimulation).
represents stimulation).


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

