Dose-response relationship between serum N-glycan markers and liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 39017915
- PMCID: PMC11461603
- DOI: 10.1007/s12072-024-10709-y
Dose-response relationship between serum N-glycan markers and liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
Background: Evaluation of liver fibrosis played a monumental role in the diagnosis and monitoring of chronic hepatitis B (CHB). We aimed to explore the value of serum N-glycan markers in liver fibrosis.
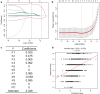
Methods: This multi-center (33 hospitals) study recruited 760 treatment-naïve CHB patients who underwent liver biopsy. Serum N-glycan markers were analyzed by DNA sequencer-assisted fluorophore-assisted with capillary electrophoresis (DSA-FACE) technology. First, we explore the relationship between 12 serum N-glycan markers and the fibrosis stage. Then, we developed a Px score for diagnosing significant fibrosis using the LASSO regression. Next, we compared the diagnostic performances between Px, LSM, APRI, and FIB-4. Finally, we explored the relationships between glycosyltransferase gene and liver fibrosis with RNA-transcriptome sequencing.
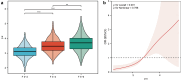
Results: We included 622 CHB participants: male-dominated (69.6%); median age 42.0 (IQR 34.0-50.0); 287 with normal ALT; 73.0% with significant fibrosis. P5(NA2), P8(NA3), and P10(NA4) were opposite to the degree of fibrosis, while other profiles (except for P0[NGA2]) increased with the degree of fibrosis. Seven profiles (P1[NGA2F], P2[NGA2FB], P3[NG1A2F], P4[NG1A2F], P7[NA2FB], P8[NA3], and P9[NA3Fb]) were selected into Px score. Px score was associated with an increased risk of significant fibrosis (for per Px score increase, the risk of significant fibrosis was increased by 3.54 times (OR = 4.54 [2.63-7.82]) in the fully-adjusted generalized linear model. p for trend was <0.001. The diagnostic performance of the Px score was superior to others. Glycosyltransferase genes were overexpressed in liver fibrosis, and glycosylation and glycosyltransferase-related pathways were significantly enriched.
Conclusions: Serum N-glycan markers were positively correlated with liver fibrosis. Px score had good performance in distinguishing significant fibrosis.
Keywords: Chronic hepatitis B; Diagnostic performance; Liver fibrosis; RNA-transcriptome sequencing; Serum N-glycan markers.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Cuiying Chen, Junli Zhang, and Chao Zhang are from Sysdiagno (Nanjing) Biotechnology Company Limited. Chi Zhang, Yiqi Liu, Lin Wang, Xueen Liu, Guiqiang Wang, Hui Zhuang, and Hong Zhao declare that they have no conflicts of interest or financial conflicts to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Global prevalence, cascade of care, and prophylaxis coverage of hepatitis B in 2022: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2023;8:879–907 - PubMed
-
- EASL. Clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2017;2017(67):370–398 - PubMed
-
- The Chinese Chapter of International Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association, Chinese Society of Liver Cancer, Society for Hepato-pancreato-biliary Surgery of Chinese Research Hospital Association SfVaToCRHA. Chinese expert consensus on antiviral therapy for hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma (2023 edition) (in Chinese). Chin J Dig Surg 2023;2023(22):29–41
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

