Electronic Health Record-Based Nudge Intervention and Axillary Surgery in Older Women With Breast Cancer: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 39018053
- PMCID: PMC11255976
- DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2024.2407
Electronic Health Record-Based Nudge Intervention and Axillary Surgery in Older Women With Breast Cancer: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Importance: Choosing Wisely recommendations advocate against routine use of axillary staging in older women with early-stage, clinically node-negative (cN0), hormone receptor-positive (HR+), and HER2-negative breast cancer. However, rates of sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) in this population remain persistently high.
Objective: To evaluate whether an electronic health record (EHR)-based nudge intervention targeting surgeons in their first outpatient visit with patients meeting Choosing Wisely criteria decreases rates of SLNB.
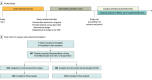
Design, setting, and participants: This nonrandomized controlled trial was a hybrid type 1 effectiveness-implementation study with subsequent postintervention semistructured interviews and lasted from October 2021 to October 2023. Data came from EHRs at 8 outpatient clinics within an integrated health care system; participants included 7 breast surgical oncologists. Data were collected for female patients meeting Choosing Wisely criteria for omission of SLNB (aged ≥70 years with cT1 and cT2, cN0, HR+/HER2- breast cancer). The study included a 12-month preintervention control period; baseline surveys assessing perceived acceptability, appropriateness, and feasibility of the designed intervention; and a 12-month intervention period.
Intervention: A column nudge was embedded into the surgeon's schedule in the EHR identifying patients meeting Choosing Wisely criteria for potential SLNB omission.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome was rate of SLNB following nudge deployment into the EHR.
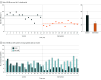
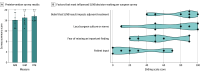
Results: Similar baseline demographic and tumor characteristics were observed before (control period, n = 194) and after (intervention period, n = 193) nudge deployment. Patients in both the control and intervention period had a median (IQR) age of 75 (72-79) years. Compared with the control period, unadjusted rates of SLNB decreased by 23.1 percentage points (46.9% SLNB rate prenudge to 23.8% after; 95% CI, -32.9 to -13.8) in the intervention period. An interrupted time series model showed a reduction in the rate of SLNB following nudge deployment (adjusted odds ratio, 0.26; 95% CI, 0.07 to 0.90; P = .03). The participating surgeons scored the intervention highly on acceptability, appropriateness, and feasibility. Dominant themes from semistructured interviews indicated that the intervention helped remind the surgeons of potential Choosing Wisely applicability without the need for additional clicks or actions on the day of the patient visit, which facilitated use.
Conclusions and relevance: This study showed that a nudge intervention in the EHR significantly decreased low-value axillary surgery in older women with early-stage, cN0, HR+/HER2- breast cancer. This user-friendly and easily implementable EHR-based intervention could be a beneficial approach for decreasing low-value care in other practice settings or patient populations.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT06006910.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment on
-
A Nudge in the Right Direction With Clinical Prompts.JAMA Surg. 2024 Oct 1;159(10):1126. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2024.2390. JAMA Surg. 2024. PMID: 39018057 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Pilewskie M, Sevilimedu V, Eroglu I, et al. How often do sentinel lymph node biopsy results affect adjuvant therapy decisions among postmenopausal women with early-stage HR+/HER2- breast cancer in the post-RxPONDER era? Ann Surg Oncol. 2022;29(10):6267-6273. doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-12193-w - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

