Precision Oncology and Systemic Targeted Therapy in Pseudomyxoma Peritonei
- PMID: 39018564
- PMCID: PMC11393541
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-4072
Precision Oncology and Systemic Targeted Therapy in Pseudomyxoma Peritonei
Abstract
Purpose: Pseudomyxoma peritonei (PMP) is a rare and poorly understood malignant condition characterized by the accumulation of intra-abdominal mucin produced from peritoneal metastases. Currently, cytoreductive surgery remains the mainstay of treatment but disease recurrence and death after relapse frequently occur in patients with PMP. New therapeutic strategies are therefore urgently needed for these patients.
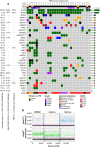
Experimental design: A total of 120 PMP samples from 50 patients were processed to generate a collection of 50 patient-derived organoid (PDO) and xenograft (PDX) models. Whole exome sequencing, immunohistochemistry analyses, and in vitro and in vivo drug efficacy studies were performed.
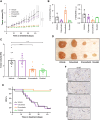
Results: In this study, we have generated a collection of PMP preclinical models and identified druggable targets, including BRAFV600E, KRASG12C, and KRASG12D, that could also be detected in intra-abdominal mucin biopsies of patients with PMP using droplet digital PCR. Preclinical models preserved the histopathological markers from the original patient sample. The BRAFV600E inhibitor encorafenib reduced cell viability of BRAFV600E PMP-PDO models. Proof-of-concept in vivo experiments showed that a systemic treatment with encorafenib significantly reduced tumor growth and prolonged survival in subcutaneous and orthotopic BRAFV600E-PMP-PDX mouse models.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates for the first time that systemic targeted therapies can effectively control PMP tumors. BRAF signaling pathway inhibition represents a new therapeutic opportunity for patients with BRAFV600E PMP who have a poor prognosis. Importantly, our present data and collection of preclinical models pave the way for evaluating the efficacy of other systemic targeted therapies toward extending the promise of precision oncology to patients with PMP.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
J. Martínez-Quintanilla reports grants from AECC during the conduct of the study; other support from Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals, Ikena Oncology, and Grifols; and grants from Vivan Therapeutics outside the submitted work. D. Cabot reports grants from AECC during the conduct of the study; other support from Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals, Ikena Oncology, and Grifols; and grants from Vivan Therapeutics outside the submitted work. D. Sabia reports grants from AECC during the conduct of the study. J. Vergés reports grants from AECC during the conduct of the study; other support from Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals, Ikena Oncology, and Grifols; and grants from Vivan Therapeutics outside the submitted work. I. Chicote reports grants from AECC during the conduct of the study; other support from Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals, Ikena Oncology, Grifols, and Alentis; and grants from Vivan Therapeutics outside the submitted work. L. Cabellos reports grants from AECC during the conduct of the study; and other support from Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals, Ikena Oncology, Grifols, Vivan Therapeutics, and Oniria Therapeutics outside the submitted work. A.M. Alcántara reports grants from AECC during the conduct of the study; other support from Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals, Ikena Oncology, and Grifols; and grants from Vivan therapeutics outside the submitted work. O. Crusellas reports grants from AECC during the conduct of the study. J. Camara reports grants from AECC during the conduct of the study. J. Barriuso reports grants from Cancer Research UK during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Ellipses Pharma, Nutricia, Rand Spa, and Medicover; non-financial support from AAA and Nanostring; and personal fees and non-financial support from Novartis, Pfizer, and Ipsen outside the submitted work. L. Nonell reports grants from AECC during the conduct of the study. R. Flores reports grants from AECC during the conduct of the study; other support from Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals, Ikena Oncology, and Grifols; and grants from Vivan Therapeutics outside the submitted work. M. Guaglio reports grants from AIRC - Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca contro il Cancro during the conduct of the study. E. Élez reports personal fees from Amgen, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cure Teq AG, Hoffman La-Roche, Janssen, Lilly, Medscape, Merck Serono, MSD, Novartis, Organon, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Repare Therapeutics Inc., RIN Institute Inc., Sanofi, Seagen International GmbH, Servier; and personal fees from Takeda and other support from Abbvie Deutschland Gmbh & Co KG, Amgen Inc., Array Biopharma Inc., AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, Bayer Pharma AG, BeiGene, Bioncotech Therapeutics, S.L., Biontech Rna Pharmacuticals GMBH, Biontech Small Molecules GMBH, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boehringer Ingelheim de España S.A., Bristol-Myers Squibb International Corporation, Daiichi Sankyo, Inc, Debiopharm International SA, Genentech Inc, Gercor, HalioDX SAS, Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Hutchinson Medipharma Limited, Hutchison MediPharma International, Iovance Biotherapeutics, Inc, Janssen Research & Development, Janssen-Cilag SA, MedImmune, Menarini, Menarini Ricerche SPA, Merck Health KGAA, Merck, Sharp & Dohme De España S.A., Merus NV, Mirati, Nouscom SRL., Novartis Farmacéutica SA, Pfizer, PharmaMar SA, Pledpharma AB, Redx Pharma PLC, Sanofi Aventis Recherche & Développement, Scandion Oncology, Seattle Genetics Inc., Servier, Sotio A.S., Taiho Pharma USA Inc., Wntresearch AB, and Celgene International SARL during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Amgen, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cure Teq AG, Hoffman La-Roche, Janssen, Lilly, Medscape, Merck Serono, MSD, Novartis, Organon, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Repare Therapeutics Inc., RIN Institute Inc., Sanofi, Seagen International GmbH, Servier, and Takeda, other support from Abbvie Deutschland Gmbh & Co KG, Amgen Inc., Array Biopharma Inc., AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, Bayer Pharma AG, BeiGene, Bioncotech Therapeutics, S.L., Biontech Rna Pharmacuticals GMBH, Biontech Small Molecules GMBH, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boehringer Ingelheim de España S.A., Bristol-Myers Squibb International Corporation, Celgene International SARL, Daiichi Sankyo, Inc, Debiopharm International SA, Genentech Inc, Gercor, HalioDX SAS, Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Hutchinson Medipharma Limited, Hutchison MediPharma International, Iovance Biotherapeutics, Inc., Janssen Research & Development, Janssen-Cilag SA, MedImmune, Menarini, Menarini Ricerche SPA, Merck Health KGAA, Merck, Sharp & Dohme De España S.A., Merus NV, Mirati, Nouscom SRL., Novartis Farmacéutica SA, Pfizer, PharmaMar SA, Pledpharma AB, Redx Pharma PLC, Sanofi Aventis Recherche & Développement, Scandion Oncology, Seattle Genetics Inc., Servier, Sotio A.S., Taiho Pharma USA Inc., and Wntresearch AB outside the submitted work. J. Tabernero reports grants from AECC during the conduct of the study; and personal fees from Alentis Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Aveo Oncology, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cardiff Oncology, CARSgen Therapeutics, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Genentech Inc, hC Bioscience, Ikena Oncology, Immodulon Therapeutics, Inspirna Inc, Lilly, Menarini, Merck Serono, Merus, MSD, Mirati, Neophore, Novartis, Ona Therapeutics, Ono Pharma USA, Orion Biotechnology, Peptomyc, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi, Scandion Oncology, Scorpion Therapeutics, Seattle Genetics, Servier, Sotio Biotech, Taiho, Takeda Oncology, Tolremo Therapeutics, Oniria Therapeutics, Alentis Therapeutics, Pangaea Oncology, 1TRIALSP, Medscape Education, PeerView Institute for Medical Education, and Physicians Education Resource (PER) outside the submitted work. O. Aziz reports grants from CRUK during the conduct of the study. M. Deraco reports grants from Italian Foundation for Cancer Research during the conduct of the study. H.G. Palmer reports grants from AECC during the conduct of the study; and non-financial support from Novartis outside the submitted work. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures




References
-
- Carr NJ, Cecil TD, Mohamed F, Sobin LH, Sugarbaker PH, González-Moreno S, et al. A consensus for classification and pathologic reporting of pseudomyxoma peritonei and associated appendiceal neoplasia: the results of the peritoneal surface oncology group international (PSOGI) modified delphi process. Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:14–26. - PubMed
-
- Wertheim I, Fleischhacker D, McLachlin CM, Rice LW, Berkowitz RS, Goff BA. Pseudomyxoma peritonei: a review of 23 cases. Obstet Gynecol 1994;84:17–21. - PubMed
-
- Mohamed F, Gething S, Haiba M, Brun EA, Sugarbaker PH. Clinically aggressive pseudomyxoma peritonei: a variant of a histologically indolent process. J Surg Oncol 2004;86:10–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

