Astrocytes require perineuronal nets to maintain synaptic homeostasis in mice
- PMID: 39020018
- PMCID: PMC11303255
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-024-01714-3
Astrocytes require perineuronal nets to maintain synaptic homeostasis in mice
Abstract
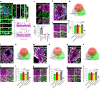
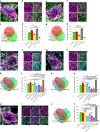
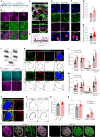
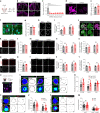
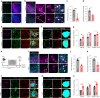
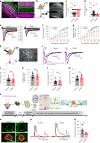
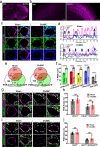
Perineuronal nets (PNNs) are densely packed extracellular matrices that cover the cell body of fast-spiking inhibitory neurons. PNNs stabilize synapses inhibiting synaptic plasticity. Here we show that synaptic terminals of fast-spiking interneurons localize to holes in the PNNs in the adult mouse somatosensory cortex. Approximately 95% of holes in the PNNs contain synapses and astrocytic processes expressing Kir4.1, glutamate and GABA transporters. Hence, holes in the PNNs contain tripartite synapses. In the adult mouse brain, PNN degradation causes an expanded astrocytic coverage of the neuronal somata without altering the axon terminals. The loss of PNNs impairs astrocytic transmitter and potassium uptake, resulting in the spillage of glutamate into the extrasynaptic space. Our data show that PNNs and astrocytes cooperate to contain synaptically released signals in physiological conditions. Their combined action is altered in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease and epilepsy where PNNs are disrupted.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









Update of
-
Perineuronal nets support astrocytic ion and glutamate homeostasis at tripartite synapses.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 2:rs.3.rs-2501039. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2501039/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nat Neurosci. 2024 Aug;27(8):1475-1488. doi: 10.1038/s41593-024-01714-3. PMID: 36778342 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Watanabe, K. et al. Three-dimensional organization of the perivascular glial limiting membrane and its relationship with the vasculature: a scanning electron microscope study. Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn.87, 109–121 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Araque, A. et al. Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci.22, 208–215 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Asztely, F., Erdemli, G. & Kullmann, D. M. Extrasynaptic glutamate spillover in the hippocampus: dependence on temperature and the role of active glutamate uptake. Neuron18, 281–293 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Parsons, M. P. & Raymond, L. A. Extrasynaptic NMDA receptor involvement in central nervous system disorders. Neuron82, 279–293 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

