Position-dependent function of human sequence-specific transcription factors
- PMID: 39020164
- PMCID: PMC11269187
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07662-z
Position-dependent function of human sequence-specific transcription factors
Abstract
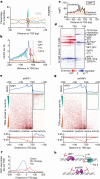
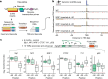
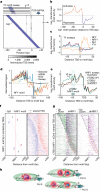
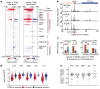
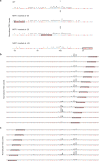
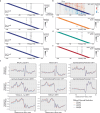
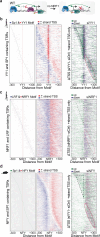
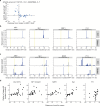
Patterns of transcriptional activity are encoded in our genome through regulatory elements such as promoters or enhancers that, paradoxically, contain similar assortments of sequence-specific transcription factor (TF) binding sites1-3. Knowledge of how these sequence motifs encode multiple, often overlapping, gene expression programs is central to understanding gene regulation and how mutations in non-coding DNA manifest in disease4,5. Here, by studying gene regulation from the perspective of individual transcription start sites (TSSs), using natural genetic variation, perturbation of endogenous TF protein levels and massively parallel analysis of natural and synthetic regulatory elements, we show that the effect of TF binding on transcription initiation is position dependent. Analysing TF-binding-site occurrences relative to the TSS, we identified several motifs with highly preferential positioning. We show that these patterns are a combination of a TF's distinct functional profiles-many TFs, including canonical activators such as NRF1, NFY and Sp1, activate or repress transcription initiation depending on their precise position relative to the TSS. As such, TFs and their spacing collectively guide the site and frequency of transcription initiation. More broadly, these findings reveal how similar assortments of TF binding sites can generate distinct gene regulatory outcomes depending on their spatial configuration and how DNA sequence polymorphisms may contribute to transcription variation and disease and underscore a critical role for TSS data in decoding the regulatory information of our genome.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH127077/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA051972/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HG011823/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA056177/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI150748/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK120515/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026929/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM149520/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 GM135515/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL147835/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI130381/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T15 LM011271/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM134366/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI106754/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135972/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM129523/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

