A combined endovascular and open repair of innominate artery bifurcation pseudoaneurysm: a case report
- PMID: 39020283
- PMCID: PMC11253463
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-024-04043-2
A combined endovascular and open repair of innominate artery bifurcation pseudoaneurysm: a case report
Abstract
Background: Innominate artery aneurysms (IAAs) are rare and may result in rupture, distal arterial embolization, or local compression without timely treatment. Rupture is the most dangerous of these complications. This article reports a case of innominate artery bifurcation pseudoaneurysm.
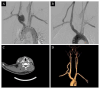
Case presentation: The patient was a 45-year-old man who was admitted to the emergency department due to chest discomfort. The computed tomographic angiography (CTA) imaging indicated the presence of a 3.6*2.4 cm saccular aneurysm in the bifurcation of the innominate artery, involving both the right proximal subclavian and common carotid arteries. The patient's vital signs were normal, there was equal blood pressure in the upper arms and no neurological dysfunction was observed. Gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography indicated that the circle of Willis was intact. The treatment involved open surgery combined with endovascular therapy. The external carotid artery was first transposed to the right subclavian artery (RSA) and an 8-mm woven Dacron graft was inserted in the middle. The covered stent graft was then placed in the proximal part of the innominate artery to close the entrance of the aneurysm. Lastly, an occluder was implanted at the origin of the RSA. There were no perioperative or postoperative complications. At 1-year follow-up, no aneurysm was observed on CTA and the right vertebral artery was patent.
Conclusions: This study indicated that the combined use of endovascular therapy and open repair surgery is an effective strategy to treat innominate artery bifurcation pseudoaneurysm.
Keywords: Endovascular repair; Hybrid technique; Innominate artery aneurysm; Occluder-covered stent-graft; Vertebral artery.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

