The Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Assessing Immediate Efficacy After Microwave Ablation of Lung Malignancies
- PMID: 39021208
- PMCID: PMC11495527
- DOI: 10.1097/RTI.0000000000000797
The Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Assessing Immediate Efficacy After Microwave Ablation of Lung Malignancies
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the imaging performance and parametric analysis of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) immediately after microwave ablation (MWA) of lung malignancies.
Materials and methods: We retrospectively analyzed the MRI performance immediately after MWA of 34 cases of lung malignancies. The ablation zone parameters of lung malignancies were measured, including the long diameter (L), short diameter (S), and safety margin of the ablation zone on plain computed tomography (CT), T1-weighted imaging (T1WI), and T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) after MWA. The study calculated the tumor volume (V 0 ), the ablation zone volume (V 1 ), and the ratio of V 0 to V 1 (V%). Statistical differences between the parameters were analyzed.
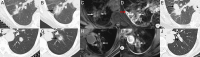
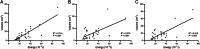
Results: The ablation area of the lesion exhibited central low signal and peripheral high signal on T2WI, central high signal and peripheral equal or high signal on T1WI, and circumferential enhancement in the periphery. The safety margin measured on T2WI was greater than that measured on plain CT and T1WI. On plain CT, the L, S, and V 1 were smaller in the effective treatment group than in the ineffective treatment group ( P <0.05). On T1WI, the V% and safety margin were greater in the effective treatment group than in the ineffective treatment group ( P =0.009 and P =0.016, respectively).
Conclusions: MRI may be a new, valuable method to assess immediate efficacy after MWA for lung malignancies using the ablation zone parameters V% on T1WI and safety margin on T2WI.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang X, Liu C, Nepal S, et al. A hybrid approach for scalable sub-tree anonymization over big data using MapReduce on cloud. J Comput Syst Sci. 2014;80:1008–1020.
-
- Venturini M, Cariati M, Marra P, et al. CIRSE standards of practice on thermal ablation of primary and secondary lung tumours. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2020;43:667–683. - PubMed
-
- Tan C, Fisher OM, Huang L, et al. Comparison of microwave and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of pulmonary metastasis of colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2022;42:4563–4571. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

