C5aR2 Deficiency Lessens C5aR1 Distribution and Expression in Neutrophils and Macrophages
- PMID: 39021433
- PMCID: PMC11254461
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/2899154
C5aR2 Deficiency Lessens C5aR1 Distribution and Expression in Neutrophils and Macrophages
Abstract
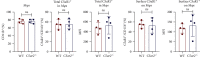
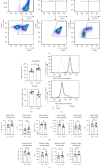
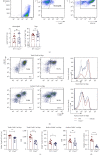
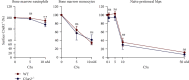
As another receptor for complement activation product C5a, C5aR2 has been paid much attention these years. Although controversial and complex, its specific signals or roles in modulating the classic receptor C5aR1 have been investigated and gradually revealed. The hypothesis of the heterodimer of C5aR1 and C5aR2 has also been suggested and observed under extremely high C5a concentrations. In this article, we tried to investigate whether C5aR2 would affect C5aR1 expression under normal or inflammatory conditions in WT and C5ar2 -/- mice of C57BL/6 background. We focused on the innate immune cells-neutrophils and macrophages. The mRNA levels of C5ar1 in normal kidney, liver, and the mRNA or protein levels of naïve-bone marrow and peripheral blood leukocytes and peritoneal Mφs were comparable between WT and C5ar2 -/- mice, indicating the technique of C5aR2 knockout did not affect the transcription of its neighboring gene C5aR1. However, the mean fluorescence intensity of surface C5aR1 on naïve circulating C5ar2 -/- neutrophils detected by FACS was reduced, which might be due to the reduced internalization of C5aR1 on C5ar2 -/- neutrophils. In the peritonitis model induced by i.p. injection of thioglycollate, more neutrophils were raised after 10 hr in C5ar2 -/- peritoneal cavity, indicating the antagonism of C5aR2 on C5aR1 signal in neutrophil chemotaxis. After 3 days of thioglycollate injection, the mainly infiltrating macrophages were comparable between WT and C5ar2 -/- mice, but the C5ar1 mRNA and surface or total C5aR1 protein expression were both reduced in C5ar2 -/- macrophages, combined with our previous study of reduced chemokines and cytokines expression in C5ar2 -/- peritoneal macrophages, indicating that C5aR2 in macrophages may cooperate with C5aR1 inflammatory signals. Our article found C5aR2 deficiency lessened C5aR1 distribution and expression in neutrophils and macrophages with different functions, indicating C5aR2 might function differently in different cells.
Copyright © 2024 Ting Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

