Baseline gut microbiota profiles affect treatment response in patients with depression
- PMID: 39021622
- PMCID: PMC11251908
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1429116
Baseline gut microbiota profiles affect treatment response in patients with depression
Abstract
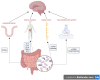
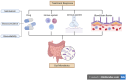
The role of the gut microbiota in the pathophysiology of depression has been explored in numerous studies, which have confirmed that the baseline gut microbial profiles of patients with depression differ from those of healthy individuals. The gut microbiome affects metabolic activity in the immune and central nervous systems and regulates intestinal ecology through the neuroendocrine system. Additionally, baseline changes in the gut microbiota differed among patients with depression who demonstrated varying treatment response. Currently, probiotics are an emerging treatment for depression; however, the efficacy of modulating the gut microbiota in the treatment of depression remains uncertain. Additionally, the mechanisms by which changes in the gut microbiota affect treatment response in patients with depression remain unclear. In this review, we aimed to summarize the differences in the baseline gut microbiota between the remission and non-remission groups after antidepressant therapy. Additionally, we summarized the possible mechanisms that may contribute to antidepressant resistance through the effects of the gut microbiome on the immune and nervous systems, various enzymes, bioaccumulation, and blood-brain barrier, and provide a basis for treating depression by targeting the gut microbiota.
Keywords: gut microbiota; gut-brain axis; major depressive disorder; psychobiotic; treatment response.
Copyright © 2024 Xie, Zhu, Yuan, Guan, Xie and Dong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Birmann P. T., Casaril A. M., Pesarico A. P., Caballero P. S., Smaniotto T., Rodrigues R. R., et al. (2021). Komagataella pastoris Km71h modulates Neuroimmune and oxidative stress parameters in animal models of depression: a proposal for a new probiotic with antidepressant-like effect. Pharmacol. Res. 171:105740. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105740, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

