Harnessing systems biology approach for characterization of carotenoid biosynthesis pathways in microalgae
- PMID: 39021674
- PMCID: PMC11252604
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101759
Harnessing systems biology approach for characterization of carotenoid biosynthesis pathways in microalgae
Abstract
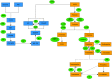
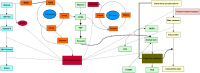
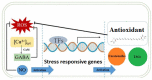
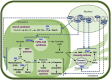
Systems biology is an interdisciplinary field that aims to understand complex biological processes at the system level. The data, driven by high-throughput omics technologies, can be used to study the underpinning mechanisms of metabolite production under different conditions to harness this knowledge for the construction of regulatory networks, protein networks, metabolic models, and engineering of strains with enhanced target metabolite production in microalgae. In the current study, we comprehensively reviewed the recent progress in the application of these technologies for the characterization of carotenoid biosynthesis pathways in microalgae. Moreover, harnessing integrated approaches such as network analysis, meta-analysis, and machine learning models for deciphering the complexity of carotenoid biosynthesis pathways were comprehensively discussed.
Keywords: Carotenoid; Microalgae; Networks; Pathway; System biology.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is not any conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kitano H. Systems biology: a brief overview. Science. 2002;295(5560):1662–1664. - PubMed
-
- Palsson B. Cambridge university press; 2015. Systems Biology.
-
- Katiyar R., et al. Microalgae: an emerging source of energy based bio-products and a solution for environmental issues. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017;72:1083–1093.
-
- Razeghi J., et al. The feasibility of microalgaeВ Dunaliella identification based on conserved regions of mitochondrial cytochrome b and cytochrome oxidase genes. Цитология и генетика. 2021;55(6):72–74.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

