BTK acts as a modulator of the response to imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 39021736
- PMCID: PMC11253089
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2024.14557
BTK acts as a modulator of the response to imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia
Abstract
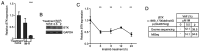
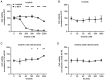
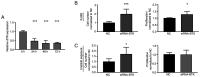
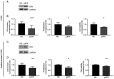
The use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors, such as imatinib, against the chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)-causing kinase BCR::ABL1 has become the model for successful targeted therapy. Nevertheless, drug resistance remains a clinical problem. Analysis of genome-wide expression and genetic aberrations of an in vitro imatinib-resistant CML cell line revealed downregulation of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK), predominantly associated with B cell malignancies, and a novel BTK kinase domain variant in imatinib resistance. This raised the question of the role of BTK in imatinib-resistant CML. In the present study, BTK downregulation and the presence of the BTK variant c.1699_1700delinsAG p.(Glu567Arg) were confirmed in imatinib resistance in vitro. Similarly, BTK inhibition or small interfering RNA-mediated BTK knockdown reduced imatinib susceptibility by 84 and 71%, respectively. BTK overexpression was detrimental to CML cells, as proliferation was significantly reduced by 20.5% under imatinib treatment. In addition, BTK rescue in imatinib-resistant cells restored imatinib sensitivity. The presence of the BTK p.(Glu567Arg) variant increased cell numbers (57%) and proliferation (37%) under imatinib exposure. These data demonstrate that BTK is important for the development of imatinib resistance in CML: Its presence increased drug response, while its absence promotes imatinib resistance. Moreover, the BTK p.(Glu567Arg) variant abrogates imatinib sensitivity. These findings demonstrate a context-dependent role for BTK as an oncogene in B cell malignancies, but as a tumor suppressor in other neoplasms.
Keywords: Bruton's tyrosine kinase; chronic myeloid leukemia; drug resistance; ibrutinib; imatinib; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Copyright © 2024, Spandidos Publications.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
