Integrating serum pharmacochemistry and network pharmacology to explore potential compounds and mechanisms of Alpiniae oxyphyllae fructus in the treatment of cellular senescence in diabetic kidney disease
- PMID: 39021818
- PMCID: PMC11251962
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1424644
Integrating serum pharmacochemistry and network pharmacology to explore potential compounds and mechanisms of Alpiniae oxyphyllae fructus in the treatment of cellular senescence in diabetic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: Diabetic kidney disease (DKD), one of the microvascular complications in patients with diabetes mellitus, is a common cause of end-stage renal disease. Cellular senescence is believed to be an essential participant in the pathogenesis of DKD. Although there is evidence that Alpiniae oxyphyllae fructus (AOF) can ameliorate DKD progression and organismal senescence, its ability to ameliorate renal cellular senescence in DKD as well as active components and molecular mechanisms remain to be explored.
Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the role of AOF in the treatment of cellular senescence in DKD and to explore its active components and potential molecular mechanisms.
Methods: The pharmacological efficacy of AOF in ameliorating cellular senescence in DKD was assessed by establishing DKD mouse models and HK-2 cells under high glucose stress. UHPLC-QTOF-MS was used to screen the active compounds in AOF, which were used in conjunction with network pharmacology to predict the molecular mechanism of AOF in the treatment of cellular senescence in DKD.
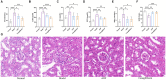
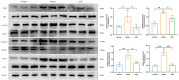
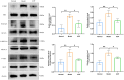
Results: In vivo experiments showed that AOF reduced GLU, mAlb, Scr, BUN, MDA, SOD levels, and ameliorated renal pathological damage and renal cell senescence in DKD mice. In vitro experiments showed that AOF-containing serum improved the decline in HK-2 cell viability and alleviated cellular senescence under high glucose intervention. The results of the UHPLC-QTOF-MS screened 26 active compounds of AOF. The network pharmacological analyses revealed that Cubebin, 2',6'-dihydroxy-4'-methoxydihydrochalcone, Chalcone base + 3O,1Prenyl, Batatasin IV, and Lucidenolactone were the five core compounds and TP53, SRC, STAT3, PIK3CA, and AKT1 are the five core targets of AOF in the treatment of DKD. Molecular docking simulation results showed that the five core compounds had good binding ability to the five core targets. Western blot validated the network pharmacological prediction results and showed that AOF and AOF-containing serum down-regulate the expression of TP53, and phosphorylation of SRC, STAT3, PIK3CA, and AKT.
Conclusion: Our study shows that AOF may delay the development of cellular senescence in DKD by down-regulating the levels of TP53, and phosphorylation of SRC, STAT3, PIK3CA, and AKT.
Keywords: Alpiniae oxyphyllae fructus; UHPLC-QTOF-MS; cellular senescence; diabetic kidney disease; molecular docking; network pharmacology; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2024 Yan, Zhang, Kang, Liu, Li, Li, Rui, Xiao and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Potential Mechanism of Alpiniae oxyphyllae Fructus Against Hyperuricemia: An Integration of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and In Vitro Experiments.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 28;17(1):71. doi: 10.3390/nu17010071. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39796505 Free PMC article.
-
[Alpiniae Oxyphyllae Fructus-Saposhnikoviae Radix regulates NLRP3 inflammasome to ameliorate inflammatory response in diabetic kidney disease mice through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 May;50(10):2798-2809. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20250214.502. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40686149 Chinese.
-
Exploring the active components and potential mechanisms of Alpiniae oxyphyllae Fructus in treating diabetes mellitus with depression by UPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap/MS, network pharmacology and molecular docking.Metab Brain Dis. 2024 Aug;39(6):1065-1084. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01374-z. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Metab Brain Dis. 2024. PMID: 38954241
-
Alpiniae oxyphyllae Fructus and Alzheimer's disease: An update and current perspective on this traditional Chinese medicine.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Mar;135:111167. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111167. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33383373 Review.
-
Probiotics improve renal function, glucose, lipids, inflammation and oxidative stress in diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ren Fail. 2022 Dec;44(1):862-880. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2079522. Ren Fail. 2022. PMID: 35611435 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Potential Mechanism of Alpiniae oxyphyllae Fructus Against Hyperuricemia: An Integration of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and In Vitro Experiments.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 28;17(1):71. doi: 10.3390/nu17010071. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39796505 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic kidney disease: from pathogenesis to multimodal therapy-current evidence and future directions.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Aug 8;12:1631053. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1631053. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40861214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting ion channel networks in diabetic kidney disease: from molecular crosstalk to precision therapeutics and clinical innovation.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 26;12:1607701. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1607701. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40641971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shenyuan granules improve cellular senescence through Klotho-mediated p16/p21 signaling pathway in diabetic kidney disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 31;12:1627412. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1627412. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40823556 Free PMC article.
-
Huangkui capsule combined with finerenone attenuates diabetic nephropathy by regulating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental verification.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Aug 4;16:1625286. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1625286. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40832613 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Magliano DJ, Boyko EJ, IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th edition scientific committee. IDF DIABETES ATLAS. 10th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation (2021).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

