Mechanism and therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine extracts in sepsis
- PMID: 39021837
- PMCID: PMC11251979
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1365639
Mechanism and therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine extracts in sepsis
Abstract
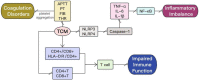
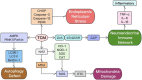
Sepsis is a complex syndrome characterized by multi-organ dysfunction, due to the presence of harmful microorganisms in blood which could cause mortality. Complications associated with sepsis involve multiple organ dysfunction. The pathogenesis of sepsis remains intricate, with limited treatment options and high mortality rates. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has consistently demonstrated to have a potential on various disease management. Its complements include reduction of oxidative stress, inhibiting inflammatory pathways, regulating immune responses, and improving microcirculation. Traditional Chinese medicine can mitigate or even treat sepsis in a human system. This review examines progress on the use of TCM extracts for treating sepsis through different pharmacological action and its mechanisms. The potential targets of TCM extracts and active ingredients for the treatment of sepsis and its complications have been elucidated through molecular biology research, network pharmacology prediction, molecular docking analysis, and visualization analysis. Our aim is to provide a theoretical basis and empirical support for utilizing TCM in the treatment of sepsis and its complications while also serving as a reference for future research and development of sepsis drugs.
Keywords: extracts; mechanism; pharmacological action; sepsis; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2024 Fu, Li, Chen, Liang, Zhao, He, Ma, Yang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
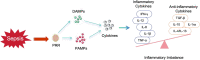
References
-
- Abu Bakar N. H., Sukari M. A., Rahmani M., Sharif A. M., Khalid K., Yusuf U. K. (2007). Chemical constituents from stem barks and roots of Murraya koenigii (Rutaceae). Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 11, 173–176.
-
- Biemond B. J., Levi M., Ten Cate H., Van Der Poll T., Büller H. R., Hack C. E., et al. (1995). Plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor I release during experimental endotoxaemia in chimpanzees: effect of interventions in the cytokine and coagulation cascades. Clin. Sci. 88, 587–594. 10.1042/cs0880587 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

