Development of an aptasensor for highly sensitive detection of cardiac troponin I using cobalt-nickel metal-organic framework (CoNi-MOF)
- PMID: 39022011
- PMCID: PMC11253065
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33238
Development of an aptasensor for highly sensitive detection of cardiac troponin I using cobalt-nickel metal-organic framework (CoNi-MOF)
Abstract
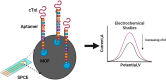
Objective and rationale: This study aimed to develop a highly sensitive and selective single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) aptamer targeting cardiac troponin I (cTnI), a crucial biomarker for acute myocardial infarction (AMI). The objective was to fabricate a novel aptamer electrochemical sensor using a composite material of cobalt-nickel metal-organic framework (CoNi-MOF) on screen-printed carbon electrodes (SPCE), leveraging the composite's large surface area and excellent electrical conductivity alongside the aptamer's high affinity for cTnI.
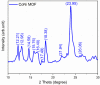
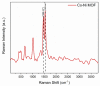
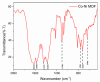
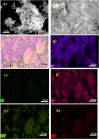
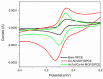
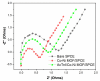
Methods: The aptamer electrochemical sensor was fabricated using the CoNi-MOF composite on SPCE and characterized its properties. They conducted electrochemical measurements to assess the sensor's performance in detecting cTnI. The sensor's stability, reproducibility, and electro-catalytic activity were evaluated.
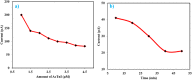
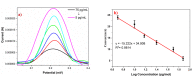
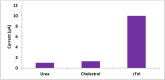
Results: The sensor demonstrated linear detection of cTnI over a concentration range of 5-75 pg/mL, with a low limit of detection (LOD) of 13.2 pM. Remarkable stability and reproducibility were observed in cTnI detection. The sensor exhibited exceptional electro-catalytic activity, enabling accurate quantification of cTnI levels in various solutions.
Conclusions: This research presents a significant advancement towards the development of reliable, cost-effective, and easily deployable cTnI sensors for clinical applications. The sensor's versatility in detecting cTnI across different concentration ranges highlights its potential utility in diverse clinical settings, particularly for early detection and monitoring of cardiac conditions.
Keywords: Aptamer; Cardiac troponin; Diagnostic sensor; Electrochemical; Metal-organic framework.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: AshokKumar Loganathan reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/501100001411Indian Council of Medical Research. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
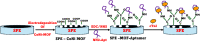
Similar articles
-
Highly sensitive amperometric detection of cardiac troponin I using sandwich aptamers and screen-printed carbon electrodes.Talanta. 2017 Apr 1;165:442-448. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2016.12.091. Epub 2016 Dec 31. Talanta. 2017. PMID: 28153281
-
Biological Recognition-Based Electrochemical Aptasensor for Point-of-Care Detection of cTnI.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jul 19;13(7):746. doi: 10.3390/bios13070746. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37504144 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical aptasensor of cardiac troponin I for the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction.Anal Chem. 2015 Oct 6;87(19):9869-75. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02312. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 26352249
-
Recent Advances in the Fabrication of Nano-aptasensors for the Detection of Troponin as a Main Biomarker of Acute Myocardial Infarction.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2023;53(3):594-613. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2021.1967721. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 34474618 Review.
-
Electrochemical strategies for the detection of cTnI.Analyst. 2021 Sep 13;146(18):5474-5495. doi: 10.1039/d1an00808k. Analyst. 2021. PMID: 34515706 Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress on nanomaterial-empowered electrochemical biosensors for the detection of cardiac troponin I.RSC Adv. 2025 Jul 23;15(32):26473-26489. doi: 10.1039/d5ra04555j. eCollection 2025 Jul 21. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40703066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptasensor-based point-of-care detection of cardiac troponin biomarkers for diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2025 Mar;41(3):e12932. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12932. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39749782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Monitoring Technologies for Cardiac Troponin I: A Pivotal Biomarker in Cardiovascular Diseases.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 12;15(6):858. doi: 10.3390/biom15060858. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40563498 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cesare M.D., Bixby H., Gaziano T., Hadeed L., Kabudula C., McGhie D.V., Mwangi J., Pervan B., Perel P., Piñeiro D., Taylor S., Pinto F. 2023. World Heart Report 2023: Confronting the World's Number One Killer; pp. 1–52.
-
- Pohanka M., Skládal P. Electrochemical biosensors - principles and applications. J. Appl. Biomed. 2008;6:57–64. doi: 10.32725/jab.2008.008. - DOI
-
- Sumitha M.S., Xavier T.S. Recent advances in electrochemical biosensors – a brief review. Hybrid Adv. 2023;2 doi: 10.1016/j.hybadv.2023.100023. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

