A matter of sex-persistent predictive value of MECKI score prognostic power in men and women with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: a multicenter study
- PMID: 39022621
- PMCID: PMC11253175
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1390544
A matter of sex-persistent predictive value of MECKI score prognostic power in men and women with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: a multicenter study
Abstract
Background: A sex-based evaluation of prognosis in heart failure (HF) is lacking.
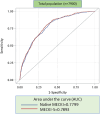
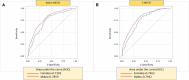
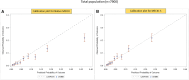
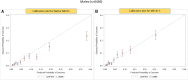
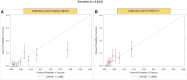
Methods and results: We analyzed the Metabolic Exercise test data combined with Cardiac and Kidney Indexes (MECKI) score registry, which includes HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) patients. A cross-validation procedure was performed to estimate weights separately for men and women of all MECKI score parameters: left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), hemoglobin, kidney function assessed by Modification of Diet in Renal Disease, blood sodium level, ventilation vs. carbon dioxide production slope, and peak oxygen consumption (peakVO2). The primary outcomes were the composite of all-cause mortality, urgent heart transplant, and implant of a left ventricle assist device. The difference in predictive ability between the native and sex recalibrated MECKI (S-MECKI) was calculated using a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve at 2 years and a calibration plot. We retrospectively analyzed 7,900 HFrEF patients included in the MECKI score registry (mean age 61 ± 13 years, 6,456 men/1,444 women, mean LVEF 33% ± 10%, mean peakVO2 56.2% ± 17.6% of predicted) with a median follow-up of 4.05 years (range 1.72-7.47). Our results revealed an unadjusted risk of events that was doubled in men compared to women (9.7 vs. 4.1) and a significant difference in weight between the sexes of most of the parameters included in the MECKI score. S-MECKI showed improved risk classification and accuracy (area under the ROC curve: 0.7893 vs. 0.7799, p = 0.02) due to prognostication improvement in the high-risk settings in both sexes (MECKI score >10 in men and >5 in women).
Conclusions: S-MECKI, i.e., the recalibrated MECKI according to sex-specific differences, constitutes a further step in the prognostic assessment of patients with severe HFrEF.
Keywords: MECKI score; heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; prognosis; risk; sex.
© 2024 Grilli, Salvioni, Moscucci, Bonomi, Sinagra, Schaeffer, Campodonico, Mapelli, Rossi, Carriere, Emdin, Piepoli, Paolillo, Senni, Passino, Apostolo, Re, Santolamazza, Magri, Lombardi, Corrá, Raimondo, Cittadini, Iorio, Salzano, Lagioia, Vignati, Badagliacca, Passantino, Filardi, Correale, Perna, Girola, Metra, Cattadori, Guazzi, Limongelli, Parati, De Martino, Matassini, Bandera, Bussotti, Scardovi, Sciomer, Agostoni and MECKI Score Research Group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor RDP declared a past co-authorship with the author GP. The authors declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Disease GBD, Injury I, Prevalence C. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. (2018) 392:1789–858. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. (2022) 145:e895–1032. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001063 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

