New Opportunities and Old Challenges in the Clinical translation of Nanotheranostics
- PMID: 39022623
- PMCID: PMC11251001
- DOI: 10.1038/s41578-023-00581-x
New Opportunities and Old Challenges in the Clinical translation of Nanotheranostics
Abstract
Nanoparticle-based systems imbued with both diagnostic and therapeutic functions, known as nanotheranostics, have enabled remarkable progress in guiding focal therapy, inducing active responses to endogenous and exogenous biophysical stimuli, and stratifying patients for optimal treatment. However, although in recent years more nanotechnological platforms and techniques have been implemented in the clinic, several important challenges remain that are specific to nanotheranostics. In this Review, we first discuss some of the many ways of 'constructing' nanotheranostics, focusing on the different imaging modalities and therapeutic strategies. We then outline nanotheranostics that are currently used in humans at different stages of clinical development, identifying specific advantages and opportunities. Finally, we define critical steps along the winding road of preclinical and clinical development and suggest actions to overcome technical, manufacturing, regulatory and economical challenges for the safe and effective clinical translation of nanotheranostics.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

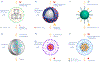
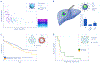

References
-
- Wagner FE; Haslbeck S; Stievano L; Calogero S; Pankhurst QA; Martinek KP, Before striking gold in gold-ruby glass. Nature 2000, 407 (6805), 691–2. - PubMed
-
- Nano on reflection. Nature Nanotechnology 2016, 11 (10), 828–834. - PubMed
-
- Weber DO, Nanomedicine. Health Forum J 1999, 42 (4), 32, 36–7. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
