PRADOC: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess the Efficiency of PRADO-IC, a Nationwide Pragmatic Transition Care Management Plan for Hospitalized Patients With Heart Failure in France
- PMID: 39023055
- PMCID: PMC11964064
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.123.032931
PRADOC: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess the Efficiency of PRADO-IC, a Nationwide Pragmatic Transition Care Management Plan for Hospitalized Patients With Heart Failure in France
Abstract
Background: The PRADO-IC (Programme de Retour à Domicile après une Insuffisance Cardiaque) is a transition care program designed to improve the coordination of care between hospital and home that was generalized in France in 2014. The PRADO-IC consists of an administrative assistant who visits patients during hospitalization to schedule follow-up visits. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the PRADO-IC program based on the hypotheses provided by health authorities.
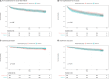
Methods and results: The PRADOC study is a multicenter, controlled, randomized, open-label, mixed-method trial of the transition program PRADO-IC versus usual management in patients hospitalized with heart failure (standard of care group; NCT03396081). A total of 404 patients were recruited between April 2018 and May 2021. The mean patient age was 75 years (±12 years) in both groups. The 2 groups were well balanced regarding severity indices. At discharge, patients homogeneously received the recommended drugs. There was no difference between groups regarding hospitalizations for acute heart failure at 1 year, with 24.60% in the standard of care group and 25.40% in the PRADO-IC group during the year following the index hospitalization (hazard ratio, 1.04 [95% CI, 0.69-1.56]; P=0.85) or cardiovascular mortality (hazard ratio, 0.67 [95% CI, 0.34-1.31]; P=0.24).
Conclusions: The PRADO-IC has not significantly improved clinical outcomes, though a trend toward reduced cardiovascular mortality is evident. These results will help in understanding how transitional care programs remain to be integrated in pathways of current patients, including telemonitoring, and to better tailor individualized approaches.
Registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov; Unique Identifier: NCT03396081.
Keywords: heart failure; mixed‐methods study; readmission; transition program.
Figures


References
-
- Le Douarin Y, Traversino Y, Graciet A, Josseran A; participants of Giens Xxxv Round Table Health e . Telemonitoring and experimentation in telemedicine for the improvement of healthcare pathways (ETAPES program). Sustainability beyond 2021: what type of organisational model and funding should be used? Therapie. 2020;2020(75):43–56. doi: 10.1016/j.therap.2019.12.009 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

