Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptors Regulate Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Neointima Formation in Mice
- PMID: 39023067
- PMCID: PMC11964046
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.124.034203
Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptors Regulate Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Neointima Formation in Mice
Abstract
Background: Vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation is involved in many types of arterial diseases, including neointima hyperplasia, in which Ca2+ has been recognized as a key player. However, the physiological role of Ca2+ release via inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (IP3Rs) from endoplasmic reticulum in regulating VSMC proliferation has not been well determined.
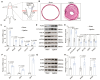
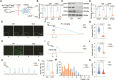
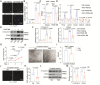
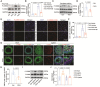
Methods and results: Both in vitro cell culture models and in vivo mouse models were generated to investigate the role of IP3Rs in regulating VSMC proliferation. Expression of all 3 IP3R subtypes was increased in cultured VSMCs upon platelet-derived growth factor-BB and FBS stimulation as well as in the left carotid artery undergoing intimal thickening after vascular occlusion. Genetic ablation of all 3 IP3R subtypes abolished endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release in cultured VSMCs, significantly reduced cell proliferation induced by platelet-derived growth factor-BB and FBS stimulation, and also decreased cell migration of VSMCs. Furthermore, smooth muscle-specific deletion of all IP3R subtypes in adult mice dramatically attenuated neointima formation induced by left carotid artery ligation, accompanied by significant decreases in cell proliferation and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in injured vessels. Mechanistically, IP3R-mediated Ca2+ release may activate cAMP response element-binding protein, a key player in controlling VSMC proliferation, via Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and Akt. Loss of IP3Rs suppressed cAMP response element-binding protein phosphorylation at Ser133 in both cultured VSMCs and injured vessels, whereas application of Ca2+ permeable ionophore, ionomycin, can reverse cAMP response element-binding protein phosphorylation in IP3R triple knockout VSMCs.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrated an essential role of IP3R-mediated Ca2+ release from endoplasmic reticulum in regulating cAMP response element-binding protein activation, VSMC proliferation, and neointima formation in mouse arteries.
Keywords: Ca2+ signaling; IP3 receptor; cell proliferation; neointima formation; vascular remodeling; vascular smooth muscle cell.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

