Increasing trend of childhood type 1 diabetes incidence: 20-year observation from Greater Poland Province, Poland
- PMID: 39023767
- PMCID: PMC11628569
- DOI: 10.1007/s00592-024-02339-5
Increasing trend of childhood type 1 diabetes incidence: 20-year observation from Greater Poland Province, Poland
Abstract
Aim: Type 1 diabetes is one of the fastest-growing chronic health conditions. Estimating the incidence rate of childhood type 1 diabetes will allow to aid in adequate planning of health care resources. The study's aim was to assess the incidence rate of type 1 diabetes in children below 15 years of age from Greater Poland (Poland) between 2006 and 2018, and then to compare obtained data to records collected between 1998 and 2003 in pediatric population aged 0-14 years from the same area.
Methods: In this cohort study covering the period from January 1998 to December 2018, data were collected for children and adolescents below 14 years of age with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes living in Greater Poland. The overall population size was taken from the Statistical Office of Poland. Total, sex-, and age-specific incidence rates per 100,000 person-years were calculated for each calendar year.
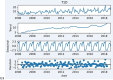
Results: Over a 20-year period, the incidence rate of type 1 diabetes in children aged 0-14 years rose around 3.6-fold, from 8.4/100,000 in 1998 to 30.8/100,000 in 2018, with the peak incidence recorded in last year of the study. A clear male predominance of type 1 diabetes was seen in all ages. The rate of type 1 diabetes incidence growth was comparable between all age groups, while the highest incidence rate was mostly observed in children aged 5-9 and 10-14 years.
Conclusions: The incidence of type 1 diabetes in children aged 0-14 years is rapidly increasing in Greater Poland.
Keywords: Adolescents; Children; Epidemiology; Incidence rate; Type 1 diabetes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008. Conflict of interest: Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gregory GA, Robinson TIG, Linklater SE et al (2022) Global incidence, prevalence, and mortality of type 1 diabetes in 2021 with projection to 2040: a modelling study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 10:741–760. 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00218-2 - PubMed
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas 2021 | IDF Diabetes Atlas. https://diabetesatlas.org/atlas/tenth-edition/. Accessed 4 Jul 2023
-
- Sussman M, Benner J, Haller MJ et al (2020) Estimated Lifetime Economic Burden of Type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 22:121–130. 10.1089/DIA.2019.0398 - PubMed
-
- Karvonen M (2006) Incidence and trends of childhood type 1 diabetes worldwide 1990–1999. Diabet Med 23:857–866. 10.1111/J.1464-5491.2006.01925.X - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

